Hauptseite/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „== '''The ACO history''' ==“) |
|||
| (129 dazwischenliegende Versionen von 3 Benutzern werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
<languages/> | <languages/> | ||
'''The | <font size=6>'''The ACO 75th Anniversary History Wiki'''</font>[[Datei:ACO Ahlmann Logo Collage 20211117.jpg|400px|thumb|right|In 1946, ACO starts operations as SAB - the Ahlmann family coat of arms with the two eels below the water level serves as the logo.]] | ||
Welcome to the ACO History Wiki, which is launched in ACO's anniversary year! | |||
The Wiki contains exciting stories about ACO. The history of the company's founding and its early years, locations and subsidiaries, products and services, employees, customers and suppliers, working life and the Ahlmann family of entrepreneurs – these are all topics that are presented in pictures covering the many years of the company’s history. Interesting correlations become clear, insights possible, and also amusing facts come to light. Here you can find out everything about how the globally-active world-market leader in drainage technology, gradually developed from small regional beginnings in Büdelsdorf in Schleswig-Holstein. | |||
The Wiki is an ongoing project that is constantly being expanded. By the 75th anniversary of the company's founding in December 2021, the first decades of the company's history is researched and documented. In the coming months, more stories and tales from and about Aco will be presented here. | |||
You are welcome to contribute to this project. Do you have pictures or documents on any aspect of ACO’s history? Can you think of any stories that are "typically ACO"? We look forward to your contributions. Contact us at: [mailto:info@history.aco info@history.aco] ! (as of December 2021) | |||
( | |||
= | <font size=5>'''The history of ACO'''</font> | ||
= ACO - Foundation and first years 1946 to 1949 = | |||
== ACO's origin: the Carlshütte == | |||
[[Datei:Holler.jpg|250px|thumb|right|Markus Hartwig Holler, Markus Hartwig Holler, the founder of Carlshütte, in his younger days.]] | |||
[[Datei:Holler.jpg|250px|thumb|right|Markus Hartwig Holler, | ACO is a spin-off from the venerable Carlshütte foundry, which is steeped in tradition, and was established in 1827 – almost 200 years ago – in Büdelsdorf near Rendsburg in Schleswig-Holstein. The Carlshütte was the very first industrial enterprise on the Jutland peninsula and, above all, the first ironworks in the whole of Denmark. The founder was the merchant Markus Hartwig Holler. He ran a flourishing timber business in Rendsburg, but wanted to build an iron foundry in Büdelsdorf. | ||
ACO | |||
Holler was completely in tune with the times. He recognized the importance of iron as a material for the new industrial era. In a petition to the Danish King Frederick VI, he meaningfully states: | |||
Holler | |||
"It is the word “iron” that explains everything". | |||
He goes on to write that iron is "equally useful, indeed indispensable, for the state and national defence, as it is for households, farmers, trades, buildings and factories. After a visit by the Danish King Frederick VI in June 1829, the King was so impressed by Holler's work, that on his return trip he issued instructions to make Holler a Knight of the Order of Dannebrog. In the picture on the right, Holler's chest shows the medal of the Order of Dannebrog, which is still awarded today as an order of merit for civil and military service to loyal servants of the Danish state, and for special merits in the arts, sciences or economic life. | |||
The Danish king's governor of the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, Carl von Hessen, supported the venture from the beginning. In gratitude, Holler named the ironworks "Carlshütte" after him. The Landgrave, who was already over 80 years old at the time of the company's foundation, was descended on his mother's side from the English royal house of Hannover, and was the father-in-law of the Danish King Frederick VI. Carl von Hessen was the great-great-great-grandfather of the recently deceased Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, Prince Consort of the British Queen Elizabeth II, who in 2006 presented ACO with "The Queen's Award for Enterprise". | |||
<br> Thus, the circle closes. | |||
[[Datei:Queens-Award entzerrt Kopie 02.jpg|250px|thumb|right| | [[Datei:Queens-Award entzerrt Kopie 02.jpg|250px|thumb|right|"The Queen and Prince Philip at the presentation of "The Queen's Award for Enterprise" to ACO in 2006.]] | ||
Carl was influenced by the ideas of the Enlightenment. He was interested in culture and science. He studied metallurgy and metal casting. He had a particular soft spot for alchemy. Thus, until the end of his life, he endeavoured to extract gold from an alloy of base metals. This passion could also have been a motive for his support of the Carlshütte. Irrespective of this, however, Carl von Hessen was regarded as an avid promoter of business and new industrial ventures. | |||
Carl | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 250 px> | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 250 px> | ||
Datei:Tischbein Carl von Hessen.jpg|<br>Carl von Hessen, | Datei:Tischbein Carl von Hessen.jpg|<br>Carl von Hessen, governor of the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, and promoter of the Carlshütte. <br> <br> | ||
Datei:Fiedrich6denmark.jpg|<br> | Datei:Fiedrich6denmark.jpg|<br>Frederick VI, the King of Denmark, also supported the Carlshütte, the first ironworks of the Danish state. <br> <br> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
The second patron and protector of the Carlshütte was the Danish King, Frederick VI. Like his governor, Carl von Hessen, he was fond of science and business. He was quickly convinced by Markus Hartwig Holler's ideas. At an audience in Rendsburg, Holler was able to present the plans for establishing the foundry in person. The king even visited the foundry construction site. | |||
Over the next ten years, Frederick VI visited the Carlshütte again and again. As in 1829 for example, when Holler was able to report on the first tapping of the smelting furnace. In 1831, Frederick VI visited the blast furnace construction site, and he was back in Rendsburg again in 1835. The king's fifth and last visit took place in 1839: the Carlshütte was in full swing, and Holler was able to present the king with a steam engine that was built there. The founder did not forget that the economic upswing was due in no small part to a number of privileges granted by the monarch. These included the duty-free import of raw materials, the duty-free export of iron goods, and protective tariffs against foreign products. | |||
However, the blast furnace only worked for a few years. The production of iron from bog iron ore, which occurs in Schleswig-Holstein in readily usable quantities, proved unprofitable, so smelting was abandoned, and the company switched exclusively to foundry operations. | |||
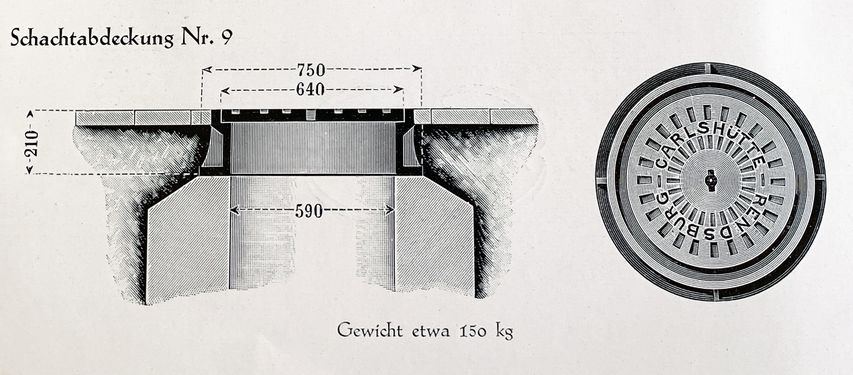
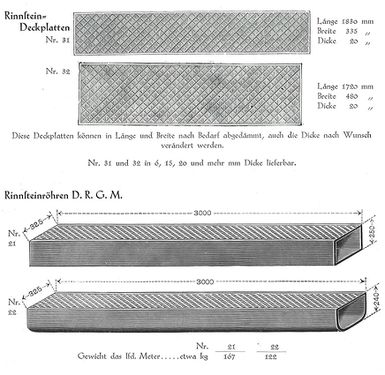
The Carlshütte produced cast-iron utensils and objects for the household, road construction, agriculture and shipbuilding. Fascinatingly, the Carlshütte had products in its range that ACO also manufactures today, albeit with different materials. These are window frames, cribs and troughs, and animal pens, also sewer and manhole covers, light oil separators, gutters with cover grates, and finally, sanitary items such as bathtubs and cast-iron water closets. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 250 px> | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 250 px> | ||
Datei:Carlshuette Gelaende ca-1860.jpg|400px|thumb|right| | Datei:Carlshuette Gelaende ca-1860.jpg|400px|thumb|right|<br> The Carlshütte in the second half of the 19th century. At the level of the sailing ship at the bottom right, one can see the foundry road leading away to the left. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Datei:Carlshuette_Produkte01.JPG|400px|thumb|right| | Datei:Carlshuette_Produkte01.JPG|400px|thumb|right|<br> Extract from a Carlshütte sample catalogue for sewer castings, late 1920s. | ||
<br> <br> | <br> <br> | ||
Datei:RinnsteinabdeckungenRoehren1.jpg|250px|thumb|right| | Datei:RinnsteinabdeckungenRoehren1.jpg|250px|thumb|right|<br> Gutter covers and channels produced by the Carlshütte. | ||
<br> <br> | <br> <br> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The Ahlmann family at the Carlshütte == | |||
The Ahlmann family was to play a key role in the development of the Carlshütte, and in the founding of ACO. The German-Danish merchant and entrepreneurial family Ahlmann has been resident in Denmark and in the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein since the 16th century. Thomas Jörgen Ahlmann, the great-great-grandfather of Hans-Julius Ahlmann, established the first connection with the Carlshütte in 1840. He went into business with Holler, and set up a commission warehouse for the Carlshütte's goods in Fredericia, Denmark. From here, Carlshütte products were distributed to the Scandinavian countries. | |||
At the time, there were no agents, but instead, wholesalers who were trusted partners. | |||
Thomas Jörgen Ahlmann also founded the distillery & brewery "Ahlmann & Co" in 1842. This company name, especially the abbreviation "ACO" , will become of particular importance more than a hundred years later. | |||
Thomas' second eldest son, Johannes Ahlmann took over his father's business together with his brother-in-law Dethlef Ohlsen, which then traded as "Ohlsen & Ahlmann" from 1878. In the following year, the two merchants moved the Carlshütte commission warehouse to Copenhagen. Hartwig Peter Holler – the son of the founder of the Carlshütte – was so convinced of Johannes Ahlmann's abilities that he offered him the post of commercial director at the Carlshütte, which he accepted in 1883. At this time, the Carlshütte was a public limited company. Over the next few decades, Johannes Ahlmann modernised the company, expanded it, and introduced new products, especially enamelled bathtubs, which made the Carlshütte world-famous. In 1900, more than 1,000 workers were employed in the company. The Copenhagen enterprise was later sold to the large Danish trading company Brødrene Dahl. | |||
In 1907, Johannes Ahlmann's son Julius joined the Carlshütte. Julius succeeded his father as commercial director in 1919, and continued the successful modernisation course. However, he died of a serious illness in 1931. His widow Käte Ahlmann was determined to preserve the company's heritage for the next generation. | |||
In 1937, she succeeded in acquiring all the shares for the family, and transformed the public limited company into a KG. Käte Ahlmann took over the management of the Carlshütte, which from then on was a family business. In the same year, parts made of asbestos cement were produced for the first time. This gave rise to a concrete division. | |||
< | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 250 px> | ||
Datei:Ahlmann Co Kopenhagen 1843.jpg|<br>"Ahlmann & Co" was the name of a distillery and brewery in Fredericia run by Thomas Jörgen Ahlmann since 1842. The distillery was later sold to De Danske Spritfabrikker.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:Ohlsen Ahlmann Marke.jpg|<br>Advertising mark of "Ohlsen & Ahlmann", 1905. The company was sold to the Danish trading company Brødrene Dahl a few years later.<br> <br>[[Datei:Kaete Ahlmann KA TITEL.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Käte Ahlmann, 1938.]]<br> <br> | |||
</ | </gallery> | ||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The beginnings of the concrete division – use of substitutes for iron == | |||
''Substitute for cast iron feet for bathtubs at the Carlshütte'' | |||
'' | |||
The forced conversion of the German economy to war production from the mid-1930s onwards gave rise to manufacturing restrictions in the steel and iron industry: metals were to be saved in the civilian sector so that they could be used for armaments. Central to this was the 1936 Four-Year Plan, with which the economic and military war capability of the German Reich was to be achieved within four years. Within the framework of the Four-Year Plan, the bathtub industry undertook to produce models with a minimum of iron components. From April 1937, the factories were ordered to no longer use cast iron feet for built-in bathtubs. The Carlshütte found a replacement in just a few months: bathtub feet and pedestals were initially made of stoneware, and later in the year they were also made of concrete. | |||
''Further savings of iron'' | |||
'' | |||
On 15 August 1937, the iron and steel supervisory authority ordered a production restriction of 30 percent compared to the production from 1 July 1935 to 30 June 1936 in the entire sanitary and sewer castings sector. This dramatically affected the Carlshütte. Initially, it was possible to fall back on stocks. Thus, from August to December 1937, the Carlshütte recorded only a 17.5 percent decline in sales of foundry products. Asbestos cement panels were used as a substitute for cast-iron underlays for continuous firing furnaces, and these were then also used for the back walls and floors of coal and gas cookers. Iron savings of 20 kg per cooker were achieved with the asbestos cement panels. The Carlshütte annual report of 1937 described the consequences of the manufacturing restrictions and bans: "The sales policy during 1937 was therefore essentially determined by the question of raw material procurement and the use or creation of adequate substitutes." | |||
''Cast terrazzo for the wash fountains, fireclay and ceramics for stoves'' | |||
'' | |||
In 1938, Carlshütte pushed ahead with the use of substitute raw materials. Terrazzo – a mixture of colour-selected aggregates, water, lime and cement – was used as cast terrazzo for the Carlshütte washing fountains, which were previously made of cast iron. For the ovens, fireclay walls were installed in place of the cast-iron walls to save iron. Further savings were achieved by using ceramic ash boxes. New to the Carlshütte range were concrete boiler stoves, which were delivered from March 1938. With the compulsory use of the new materials, which were not characteristic of an iron foundry, a concrete division was set up at the Carlshütte, from which the Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB), later ACO Severin Ahlmann, was established. | |||
1938 | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 270 px> | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 270 px> | ||
Datei:Carlshuette_Produkte02.JPG|<br> | Datei:Carlshuette_Produkte02.JPG|<br>Bathtub brochure from 1914: The feet always had to be ordered separately. The cast iron was replaced here from 1937, first by stoneware, then by concrete. <br> <br> . | ||
Datei:Carlshuette_Produkt03_Carola2.jpg|<br> | Datei:Carlshuette_Produkt03_Carola2.jpg|<br>The Carola Washing Fountain No. 8 was a successful Carlshütte product in the 1930s. It was made of enamelled cast iron. <br> <br> | ||
Datei:Terrazzo Waschbrunnen KA 4 16 jp.jpg|<br> | Datei:Terrazzo Waschbrunnen KA 4 16 jp.jpg|<br>The washing fountain in terrazzo design: in December 1937, the cast-iron base was first replaced by stoneware and terrazzo to save iron. Then the fountains were made almost entirely of "marble granules". (image source: LASH) <br> <br> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Josef-Severin Ahlmann – responsible for the concrete division at the Carlshütte. == | |||
[[Datei:Leutnant Severin Ahlmann KA 5 10a .jpg|300px|thumb|right|Severin Ahlmann, ca. 1944/45, at the foot of the garden steps of the directors' house. He was visiting his grandmother Wilhelmine Ahlmann.]] | |||
[[Datei:Leutnant Severin Ahlmann KA 5 10a .jpg|300px|thumb|right|Severin Ahlmann, ca. 1944/45, | The Second World War broke out in 1939. Käte Ahlmann's sons Hans-Julius and Josef-Severin were called up for military service. The factory survived the war largely unscathed. In May 1945, Käte Ahlmann's second-born son Josef-Severin returned from the war. Schleswig-Holstein, including Büdelsdorf, was part of the British occupation zone. | ||
1939 | |||
The Carlshütte family business was subject to production restrictions imposed by the military government. However, it was allowed to produce concrete parts for civilian purposes. These were "simple building slabs", agricultural troughs and cement roof tiles. | |||
Josef-Severin immediately took over management tasks in the company on behalf of his mother. He took care of the concrete production at the Carlshütte. At the age of 22, he became department head of the Carlshütte concrete division. | |||
Josef-Severin | |||
Severin's brother Hans-Julius also returned from captivity at the beginning of 1946. He had already had power of attorney for several years, and was designated by his mother as her successor in the management of the Carlshütte. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 370 px> | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 370 px> | ||
Datei:HollerHaus2.jpg|<br> | Datei:HollerHaus2.jpg|<br>On 8 May 1945, Rendsburg and Büdelsdorf were occupied by British troops. The British commandeered Käte Ahlmann's house, and converted it into an officers' mess. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Establishment of Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB), later ACO == | |||
In the course of 1946, Käte Ahlmann, and Hans-Julius and Severin Ahlmann, decide to spin off the concrete division from the Carlshütte as an independent company. The background to this was fear that the Carlshütte would be dismantled by the Allies. On 1 October 1946, the British military government informed the Carlshütte management that the plant was earmarked for dismantling as part of the reparation demands. | |||
The specific reason for the timing of the company establishment before the end of the year was the result of the local elections in Schleswig-Holstein on 13 October 1946, in which the SPD won 41.1 percent of the vote. It was assumed that the Social Democrats would also gain a majority in the state elections scheduled for the following year. The worry was that they would implement expropriation plans. The Social Democrats and the trade unions propagated the expropriation of key industries or companies that were involved in the armaments industry during the Second World War, including the Carlshütte. Käte Ahlmann wrote in a letter on 13 December: "We thought this measure (meaning the company registration) was still the right thing to do in the old year, since one never knows what new prohibitions will come at the end of this year." | |||
In order to secure at least one segment of the business for the family, Josef-Severin Ahlmann registered the company "Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie" with the Kiel Chamber of Industry and Commerce on 10 December 1946. SAB, as the company name was abbreviated, later became ACO. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 467 px> | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 467 px> | ||
Datei:1.1.A 00000 19461001 AhlmannCarlshütte,003 .jpg|<br> | Datei:1.1.A 00000 19461001 AhlmannCarlshütte,003 .jpg|<br>An impressive letter from the Carlshütte works council arguing passionately against the planned dismantling of the company. <br> <br> | ||
Datei:1.1.A 00000 19461001 AhlmannCarlshütte,004.jpg|<br> | Datei:1.1.A 00000 19461001 AhlmannCarlshütte,004.jpg|<br> It was dated 5 October 1946: which meant that the workforce reacted to protect their Carlshütte just four days after the British plans for dismantling became known. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
[[Datei:1944KielHoltenauerStrasse.png|320px|thumb|right| | |||
== The product range of Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB, later ACO) == | |||
[[Datei:1944KielHoltenauerStrasse.png|320px|thumb|right|Kiel in ruins in September 1944 as a result of aerial bombing. The view of the Holtenauer Straße shows the extent of the destruction. (Image source: Kiel City Archives, Sig. 36.311)]] | |||
It was clear from the company registration letter that the production of new articles was to be started step by step. Three product groups were mentioned: Firstly, building materials for house construction: such as hollow blocks, slabs and lightweight panels, beams and rafters, as well as stair treads. Furthermore, products for civil engineering were also to be manufactured. These included posts, pavement slabs, kerbstones, pipes and cable fittings, driven piles, as well as manhole covers, street drains, cesspits and septic tanks. Finally, it was planned to also produce "non-building materials", meaning products for interior finishing, such as concrete boiler stove jackets and, in particular, terrazzo goods, such as sinks and washbasins. | |||
The articles of the first and second product group were the main priority, explained Severin Ahlmann, because they were "particularly important for the reconstruction of the destroyed cities". In Kiel, for example, 35 percent of all buildings were destroyed, 40 percent were damaged. In the future expansion of labour, more women were to be employed. Production was to be set up accordingly. | |||
The letter concludes with a reference to good order prospects because the Carlshütte intended to successively transfer the entire concrete production to the new Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 350 px> | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 350 px> | ||
Datei:Firmenanmeldung 1946 Seite1.jpg|<br> | Datei:Firmenanmeldung 1946 Seite1.jpg|<br>The registration of SAB, later ACO, with the Kiel Chamber of Industry and Commerce on 10 December 1946. <br> <br> | ||
Datei:Firmenanmeldung 1946 Seite2.jpg|<br> | Datei:Firmenanmeldung 1946 Seite2.jpg|<br>Here Severin Ahlmann lists the planned production programme of Severin Ahlmann- Betonindustrie (SAB, later ACO).<br> <br> | ||
Datei:BriefbogenmitKopfundTextausschnitt.jpg|<br> | Datei:BriefbogenmitKopfundTextausschnitt.jpg|<br>On 17 December 1946, a week after the establishment of the company, Käte Ahlmann wrote to her brother-in-law Hanno Athenstaedt on a letterhead from SAB: "You see the new company on this sheet! May it be lucky! All the permits are there, except for the trade licence from the city of Rendsburg." <br> <br> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 300 px> | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 300 px> | ||
Datei:Behörde Gewerbeanmelde-Bescheinigung 1946.jpg|<br> | Datei:Behörde Gewerbeanmelde-Bescheinigung 1946.jpg|<br>The company registration at the Kiel Chamber of Industry and Commerce was processed quickly. The trade registration certificate with the number 891/46 for the trade "concrete industry" – the birth certificate of ACO, so to speak – was issued on 19 December 1946. The retroactive effect to the 10th of the month was noted. <br> <br> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== | |||
== Company headquarters in Rendsburg - production facilities in Büdelsdorf == | |||
The company's first registered office was not in Büdelsdorf, but Rendsburg. The address was Holsteiner Straße 24, where the Carlshütte kindergarten was also located. Severin Ahlmann later liked to say:"ACO was founded in a kindergarten on an Eider lock." The address – some distance from the Carlshütte – underlines the character of an independent establishment. It was a strategic decision vis-à-vis the authorities. | |||
The production facilities, however, were located on Hüttenweg in Büdelsdorf on the Carlshütte site. Käte Ahlmann leased the site and buildings to SAB. | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 250 px> | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 250 px> | ||
Datei:Kindergarten Zander 1.jpg| | Datei:Kindergarten Zander 1.jpg|<br> The first company headquarters at Holsteiner Straße 24 in Rendsburg. Gesa Meyer, the daughter of the first managing director Paul Meyer, was one of the kindergarten children at the time and recalls: "Our father's office was on the ground floor, to the left of the main entrance, and just behind it was Josef-Severin Ahlmann's office, with a wonderful soft, dove-blue carpet." <br> <br> | ||
Datei:SchleuseKindergartenZander003.jpg|<br> | Datei:SchleuseKindergartenZander003.jpg|<br> The Kronwerk lock in Rendsburg linking the Obereider to the Untereider. In the background on the left is the building that was the first headquarters of Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie in 1946. <br> <br> | ||
<br> <br> | <br> <br> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Workforce and products == | |||
= | |||
[[Datei:1.1.B 00055 Severin Ahlmann,07a.jpg|280px|thumb|right| The young Severin Ahlmann and Paul Meyer.]] | |||
[[Datei:1.1.B 00055 Severin Ahlmann,07a.jpg|280px|thumb|right| | Carlshütte and SAB were closely connected. Friedrich Sensen, Käte Ahlmann's deputy at the Carlshütte, recommended his brother-in-law Paul Meyer as an authorised signatory and de facto managing director of SAB. Meyer had a decisive influence on the company in the early years at Severin Ahlmann's side. He was instrumental in SAB's success. | ||
At the time of the company's registration, SAB had only eleven employees. Soon the number of employees rose to 100. From the beginning, Severin Ahlmann employed refugees and displaced persons from the former German eastern territories, and the Soviet occupation zone. They became a success factor for the young company. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 250 px> | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 250 px> | ||
Datei:Laster_vor_Werksgelände_1950.jpg|<br> | Datei:Laster_vor_Werksgelände_1950.jpg|<br>Water management production factory of Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie in Büdelsdorf, with truck and trailer, and the driver Mr Bruhn, 1949. <br> <br> | ||
Datei:1.1.B 00087 19491224 SeverinAhlmann,45.jpg|<br> | Datei:1.1.B 00087 19491224 SeverinAhlmann,45.jpg|<br>View of the marble granule polishing shop in factory building VI. <br> <br> | ||
Datei:1.1.B 00087 19491224 SeverinAhlmann,40.jpg|<br> | Datei:1.1.B 00087 19491224 SeverinAhlmann,40.jpg|<br>Exhibition room "Glück-Auf" of the Carlshütte with marble granule products of Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB, later ACO). <br> <br> | ||
Datei:1.1.B 00087 19491224 SeverinAhlmann,38.jpg|<br> | Datei:1.1.B 00087 19491224 SeverinAhlmann,38.jpg|<br>Mr Biemann and Ms Jechura in the office. The logo of Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB, later ACO) is clearly visible on the window pane. <br> <br> | ||
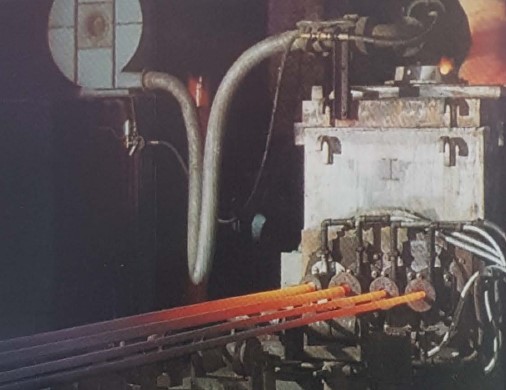
Datei:1.1.B 00087 19491224 SeverinAhlmann,48.jpg| | Datei:1.1.B 00087 19491224 SeverinAhlmann,48.jpg|<br> The warehouse (factory building IV) at SAB. Concrete roof tiles can be seen on the right. For the British Rhine-Army and other British services, Carlshütte produced 42,000 stoves in 1945/46, 40,000 Canada stoves, 40,000 cookers, 100 large cookers, 3,500 bath tubs, 10,000 radiators, 5,000 washing kettles and also 50,000 aluminium roof tiles. Concrete was also used for roof tiles. This production was done on a large scale by SAB. Concrete roof tiles are an important product for SAB. Gerd Ostryga, who started at the Carlshütte on 17 November 1946, and shortly afterwards moved to the new Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB, later ACO), recounts in his memoirs that one of his first tasks was to form concrete roof tiles. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The first logo of SAB (later ACO) == | |||
The first logo of the newly founded Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie consisted of a coat of arms with stylised Ahlmann lettering. The coat of arms originally came from Bankhaus Ahlmann in Kiel, and was used by Severin Ahlmann to highlight the long family tradition. The logo was later used as a model for the logos of other Ahlmann companies. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 270 px> | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 270 px> | ||
Datei:Logo 001.jpg|<br>Das | Datei:Logo 001.jpg|<br>The first logo of Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie. <br> <br> | ||
Datei: | Datei:ProdukteLogo.jpg|<br>Concrete products of the young SAB featuring the logo. <br> <br> | ||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Work under difficult conditions == | |||
[[Datei:Behörde Fernsprechverkehr Antrag Dez1946.jpg||300px|thumb|right|Voice telephony was requested by SAB, which the authorities do not approve until five months later.]] | |||
The production permit for SAB did not arrive until March 1947. Until then, the permit issued to the Carlshütte was valid. | |||
Production was by no means easy in the post-war period. There were shortages everywhere. This applied to food and everyday items, as well as to raw materials and energy. Parts of the infrastructure were still not repaired. Almost all resources were regulated by the authorities. | |||
At the end of March 1947, the city of Rendsburg allocated SAB a certain amount of electricity: 15,000 kWh per month. | |||
In mid-May 1947, the Rendsburg post office informed Severin Ahlmann that his application for "Permission for unrestricted voice telephony within the British zone" was granted. He had to wait a long time for this: the application had been submitted six months earlier. Severin Ahlmann was able to keep an existing telephone number - 2555. In addition, he was given the opportunity to register for call prioritisation by dialling a specific code number. | |||
== The foundation of Ahlmann & Co. in Andernach == | |||
[[Datei:Bild6.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Iron foundry and enamelling works of Ahlmann & Co. in Andernach after completion. Construction work began in May 1949.]] | |||
On 1 November 1948, Ahlmann & Co. was founded in Andernach, Rhineland-Palatinate. The aim of establishing this company – similar to the establishment of Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie two years earlier – was to secure the family and its entrepreneurial activities in view of the uncertain political and economic future. Andernach was located in the French occupation zone. It was hoped that dismantling and expropriation plans would be pursued less intensely here, or not at all. Moreover, Käte Ahlmann, who comes from the Rhineland, had close ties to the region. | |||
Another reason for the Ahlmann family to hedge their bets was the beginning of the "Cold War". The blockade of Berlin by the Soviet Union fuelled the fear of escalation. Andernach, which was further away from the East Zone border, and lay mainly on the other side of the Rhine, appeared to be a "safe fallback location" in case the Red Army advanced to the Rhine. | |||
Purely economic motives also played a role. An iron foundry and an enamelling plant were to be built in Andernach. The product range corresponded to that of the Carlshütte: cast iron tubs, washers and other sanitary castings. The new plant was an extension of the Carlshütte, which was to supply the French and American zones with these products. | |||
The project was approved at the beginning of February. At the end of May 1949, construction work began and progressed rapidly. In the following years, there was an exchange of personnel between Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB) and the newly founded company in the Rhineland. This was accompanied by a fruitful transfer of know-how. | |||
Another important aspect: Ahlmann & Co. later provided the abbreviation for the group's current name: ACO. Josef-Severin Ahlmann later recalled that the business liked to refer to Thomas Jörgen Ahlmann's company Ahlmann & Co. established in Fredericia in 1842. | |||
[[Datei:Bild7.jpg||300px|thumb|right|Maria Luise and Severin Ahlmann in the SAB director's office. Severin's wife was involved in the company.]] | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== SAB in 1949 == | |||
Käte Ahlmann was exonerated in the denazification proceedings, the accounts were unblocked, the Carlshütte was not dismantled. | |||
However, a reincorporation of concrete production into the Carlshütte was not an issue. SAB remained an independent company, had made a name for itself, and was growing. In 1949, the turnover was DM 665,000, more than four times the turnover two years earlier. The number of customers doubled in the same period. In 1949 there were 550. | |||
Severin Ahlmann had married in the meantime. His wife Maria Luise, née Guthe, worked in the company. A photo album made by Severin Ahlmann in 1949 gives an insight into the early days of the company. | |||
[[Special:MyLanguage/Das SAB-Fotoalbum 1949|You can browse through the entire photo album here.]] | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 350 px> | |||
Datei:Fotoalbum Einband.jpg|<br>Cover of the photo album compiled by Severin Ahlmann three years after the founding of SAB. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:1.1.B 00087 19491224 SeverinAhlmann,04.jpg|<br>Severin's dedication to his mother Käte Ahlmann. He wrote: "To our mother! 'We don't celebrate anniversaries - we celebrate successes!' We also want to claim this saying for ourselves, and can state with satisfaction that the foundations for the future have been laid. With heartfelt gratitude for entrusting us with this ongoing task. Your Josef-Severin. 24.12.1949" <br> <br> | |||
Datei:Inhaltsverzeichnis Fotoalbum JSA.jpg|<br>Table of contents of the photo album from December 1949. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:InhaltsverzeichnFotoalbumJSAAusschnittt.jpg|<br>""Whether stone or cast, when it’s from AHLMANN it will last!" An advertising slogan representing both the Carlshütte and Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB, later ACO). | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
= Severin Ahlmann's involvement in the Carlshütte and SAB (ACO) 1949 to 1956 = | |||
== The business development of SAB (ACO) in the early 1950s == | |||
[[Datei:1.1.A-00504 19510310 Produktionsgelaende 01.jpg|500px|thumb|right|The SAB site on Vorwerksallee in the early 1950s.]] | |||
The young SAB developed extremely positively in the early years. At the end of the fourth business year in 1950, the turnover of DM 1,600,000, was ten times that of the first full year in 1947. The customer base had almost quintupled in this short time, to 965. Most of the customers still came from northern Germany, from Schleswig-Holstein and the Hamburg area. However, Severin Ahlmann announced as early as 1951 that the company had "increasingly succeeded in opening up the German markets south of the Elbe." | |||
By 1951, the workforce had grown from the initial eleven employees to around 100, confirming the positive trend. | |||
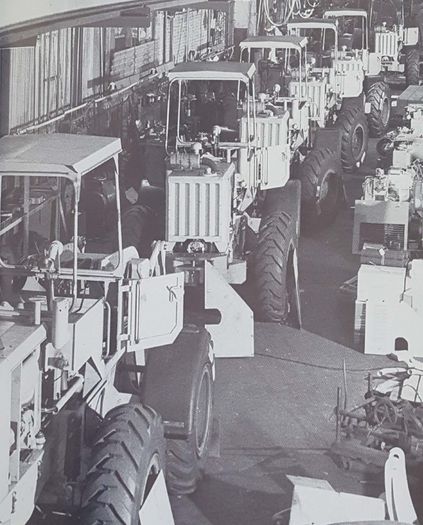
Whereas at the very beginning, large orders from customers could often not be processed due to the limited production capacities, this situation improved at the beginning of the 1950s. There was major investment: new, modern machines made higher order volumes possible. And if production also had more space to develop, then even more could be made. | |||
In the spring of 1951, the company founder emphasised the "importance of our company in the Rendsburg economic region". The local and state authorities saw it similarly, and supported the young company; this was also because Severin Ahlmann had tailored his production to urgent, very current problems: SAB manufactured the articles needed for reconstruction. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 350 px> | |||
Datei:Freluftlager Hoffmannschnecke.jpg|<br>Outdoor storage of products made of heavy concrete on the Eider: in this case, Hofmann spirals. In the background you can see the elms at the rear of the car park, which were still young then, and are now fully grown trees. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:Hoffmann Trennschnecke.jpg|<br>A special product of the first SAB years: the so-called Hoffmann separating spiral for domestic sewage treatment plants is cast from concrete. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Securing raw materials - the acquisition of the Mielberg gravel plant == | |||
[[Datei:Kieswerk Mielberg ab1950.jpg|400px|thumb|right|The Mielberg gravel works acquired by SAB in 1950.]] | |||
In 1950, SAB secured the future supply of aggregate. This is the term used to describe mineral additives - from sand to gravel – that, when combined with water and cement as a binding agent, produce concrete. | |||
In February 1950, Severin Ahlmann acquired the gravel plant in Mielberg, municipality of Jagel, in Schleswig, from Struve & Weyhe. The purchase included a workshop, a silo, various machines, such as scraper and screening plants, conveyor belts, pumps and electric motors, as well as a range of small equipment. And it also included the production rights. In 1943, Struve & Weyhe had concluded an extraction contract for a plot of land of about three hectares belonging to the Mielberg farmer Johann Gerold. This allowed the company to extract stones, gravel and sand from the ground there. | |||
SAB took over all existing delivery obligations, as well as the employment contracts of those who had been working in the gravel pit before the takeover. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Entrepreneurial activities of the Ahlmanns in the young Federal Republic of Germany == | |||
[[Datei:1.1.A 00000 195010NN GlückAufACH,002.jpg|320px|thumb|right|Three blocks of flats just completed by the Gemeinnützige Wohnungsgesellschaft A GmbH on the Elchstraße in Büdelsdorf. The first flats were ready for occupancy in October 1950. On the right in the picture is a hut from the former makeshift housing estate.]] | |||
For Severin Ahlmann in the 1950s, however, SAB is "only" one building block in a company complex centred on the Carlshütte. | |||
After the plans to dismantle and expropriate the Carlshütte had been averted, Käte Ahlmann devoted herself to a wealth of new activities. In doing so, the now almost sixty-year-old businesswoman unleashed an enormous amount of energy. Her sons Severin and Hans-Julius were also involved with passion and vision. | |||
To help alleviate the still acute housing shortage, the family founded the "Gemeinnützige Wohnungsgesellschaft A GmbH" in early 1949. In addition to the Carlshütte, Severin's SAB also financed the new company, which primarily created cheap housing for the many displaced persons. In September 1949, the topping-out ceremony for the first construction phase of a housing estate with 36 flats was celebrated. | |||
With the upswing of the Carlshütte, and the good economic development of SAB, the transport volume also increased. As a consequence, Ahlmann-Transport KG was founded in September 1950. The company was entered in the commercial register on 25 October 1950, with Severin Ahlmann as the owner, and his brother Hans-Julius as the authorised signatory. Branches were opened in Hamburg and Bremen. The new company transported goods by truck and rail. It also loaded ships. And what's more: Ahlmann-Transport KG also acted as a shipping company, running scheduled services, and commissioning the construction of ships, which are used in a variety of ways. Friedrich Sensen, Kätes' confidant and the grey eminence of the Carlshütte, played a decisive role as managing director of Ahlmann Transport KG. | |||
There are three main reasons for the investment in ships: the Carlshütte is located far away from its sources of raw materials, and partly also from the areas where its products were sold. A major advantage, however, is its location on the Upper Eider, with access to the Kiel Canal. It also had a history of shipbuilding. A factory-owned shipyard was built on the Eider in 1847, and it had traditionally maintained a number of ships bearing the name "Carlshütte" with consecutive numbers. After the Second World War, the German merchant fleet was destroyed, and was to be rapidly rebuilt by German companies. The creation of new shipping capacities was therefore fiscally subsidised. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 350 px> | |||
Datei:Skizzenbuch Ahlmann Transport KG.JPG|<br>The activities of Ahlmann-Transport KG at a glance.<br> It maintained a fleet of trucks and also acted as a shipping company.<br> Top left: the flag under which the ships sailed. <br> <br> . | |||
Datei:Schiff Hochbrücke.tif|<br>The COLONIA, a ship in the Ahlmann fleet, passing under the Rendsburg High Bridge. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 300 px> | |||
Datei:LKW Ahlmann Transport.png|<br>Truck of the Ahlmann Transport company in the mid-1950s. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:Eisenkunstgussplakette.jpg|<br>An aircraft, truck, ship and train circle the Ahlmann coat-of-arms: cast iron plaque from 1960 marking the 10th anniversary of Ahlmann-Transport KG. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The overseas connections == | |||
[[Datei:Übergabe Ciandra an JSA.jpg|300px|thumb|right|The CIANDRA being handed over to Severin Ahlmann (right in the picture).<br> The ship's funnel features the company logo of the Ahlmann enterprises at the time, with the two eels below the waterline.]] | |||
Further steps in the transport business follow: in April 1951, Translanta GmbH was founded as an independent shipping company. The company was based in Rendsburg. | |||
New ships were also built especially for Translanta: the ocean-going vessels COLONIA and CIANDRA, commissioned in 1952 and 1953. | |||
The ships were equipped with "particularly nicely furnished passenger cabins". The salons designed by Severin with mirrored floors and cowhide rugs, which came from cows on the Ahlmann farm on the Carlshütte that grazed where the "Rondo" is today, caused a sensation. Of course, the bathtubs from the foundry are not missing either – at that time an almost unheard-of luxury on ships of this class. | |||
The COLONIA and CIANDRA sailed on the Ahlmann Trans Caribbean Line from the Great Lakes in Canada to the Caribbean: the first route for German ships between foreign ports in the post-war era. | |||
Severin Ahlmann traveled a lot on business during this time, especially to the USA and Canada. In just two years he flew more than 500 hours. The aim was to catch up with international developments, and to position the name "Ahlmann" worldwide. On the one hand, together with managers from the Carlshütte, he informed himself in detail about the latest developments in the field of foundry technology and the enamelling industry, as well as in mechanical and plant engineering. On the other hand, new sales markets were to be opened up after those in Eastern Europe were lost behind the Iron Curtain. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 350 px> | |||
Datei:Industriemesse USA 1951.png|<br>Just a few years after the end of the war, Carlshütte is once again fully present overseas, as here with a booth at the Great New York State Fair in 1951.<br> | |||
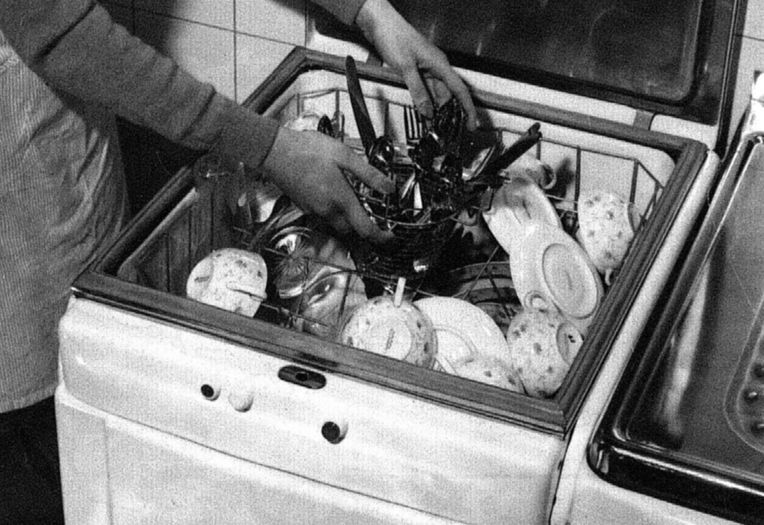
Datei:Geschirrspuelmaschine KA 6 10b.jpg|<br>Dishwashing machines were already being developed at Carlshütte in the early 1950s. The idea originated in the USA. For Europe, however, the innovation comes too early - there is not a market for appliances of this kind yet. (image source: LASH) | |||
<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
In 1951, in the small town of Grand-Mère, in Quebec province in Canada, Severin Ahlmann and an American partner set up Adanac Foundry Industries Ltd, the Canadian subsidiary of the Carlshütte. Hans Schlothfeldt, the foundry manager at the Carlshütte for many years, took over the operational development of the local plant. Grand-Mère marked the beginning of the globalisation of Ahlmann's ventures, which will also play a big role for ACO: a paradigm is established that laid the foundations the later "ACO worldwide". | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 800 px> | |||
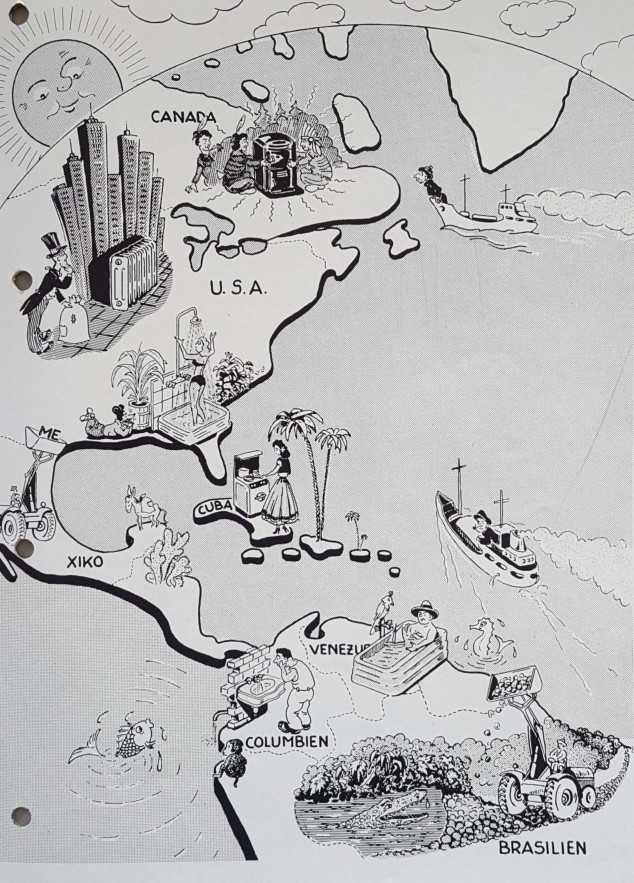
Datei:Ahlmann auf Reisen Gluek auf April 1954.jpg|<br>The 1950s-style illustration of Severin Ahlmann's numerous overseas travels and activities appeared in April 1954 in "Glück auf", the Carlshütte's in-house magazine. This shows an Ahlmann stove in Canada, radiators and shower trays in the USA. While in Mexico and Brazil, Ahlmann bucket loader are at work, and ships of the Ahlmann fleet are sailing in the Atlantic. In 1954, there were already rudiments of what ACO does today in the Americas. The vision of that time has become a reality. | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Death of the heir apparent - birth of a new heir in 1952 == | |||
On the way back from an inspection trip to the Lürssen shipyard in Bremen, Severin's brother Hans-Julius Ahlmann suffered a serious car accident. He lost control of his car and hit a bridge pillar. In hospital he suffered a pulmonary embolism due to shattered tubular bones. He died on 8 January 1952, one month before his 33rd birthday. The family is totally shocked. Many hopes had been pinned on Käte Ahlmann's eldest son. He was already established as a successor in the Carlshütte company. | |||
Three months later, his widow Juliane gave birth to Hans-Julius' son on 14 April 1952. The son is baptized and given his father's name. On 19 April, which has always been celebrated as Foundry Day, the Carlshütte celebrated its 125th anniversary. Severin Ahlmann was now to be appointed as the successor to the family business. Therefore, Käte Ahlmann asked her daughter-in-law, while still in puerperium, to transfer all the new-born’s company shares to Severin. Juliane accepted, and so Josef-Severin Ahlmann entered a new creative phase with extended powers. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 350 px> | |||
Datei:HJAsen 1952 Todesanzeige.jpg|<br> Invitation to the funeral service for Hans-Julius Ahlmann on 12 January 1952. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:Geburtsanzeige HJA.jpg|<br>Birth announcement for Hans-Julius Ahlmann. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:Glück auf 125 Jahre CH.jpg|<br>Black sky over the Eider: the anniversary edition of the "Glück auf" magazine, on the occasion of the 125th anniversary of the Carlshütte, was published for Foundry Day in April 1952. The gloomy design of the cover reflects the mourning of the death of Hans-Julius Ahlmann a few months earlier. <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 300 px> . | |||
Datei:Juliane Grün und HJA junior.jpg|<br>Juliane Ahlmann with her son Hans-Julius. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:Käte und HJ Ahlmann CH Mitte 1950er.jpg|<br>Käte Ahlmann with her grandson Hans-Julius on the grounds of the Carlshütte.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The further development of the SAB (ACO) company premises == | |||
In 1952, Severin Ahlmann acquired a site from the town of Rendsburg, which enabled SAB to expand decisively. | |||
Just a few months after the start of SAB, it had become clear that the company needed more space for manufacturing. In the second half of 1947, Severin Ahlmann leased space from the neighbouring timber trading company H.F. Timm. This was only a sublease, as Timm itself had leased the land from the owner, the town of Rendsburg. | |||
SAB initially acquired land to the east of H.F. Timm on a so-called expansion site. The tracks of the Carlshütte works railway cut through this area on the northern bank of the Eider. Now the SAB site almost completely surrounded the Timm timber business. | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 400 px> | |||
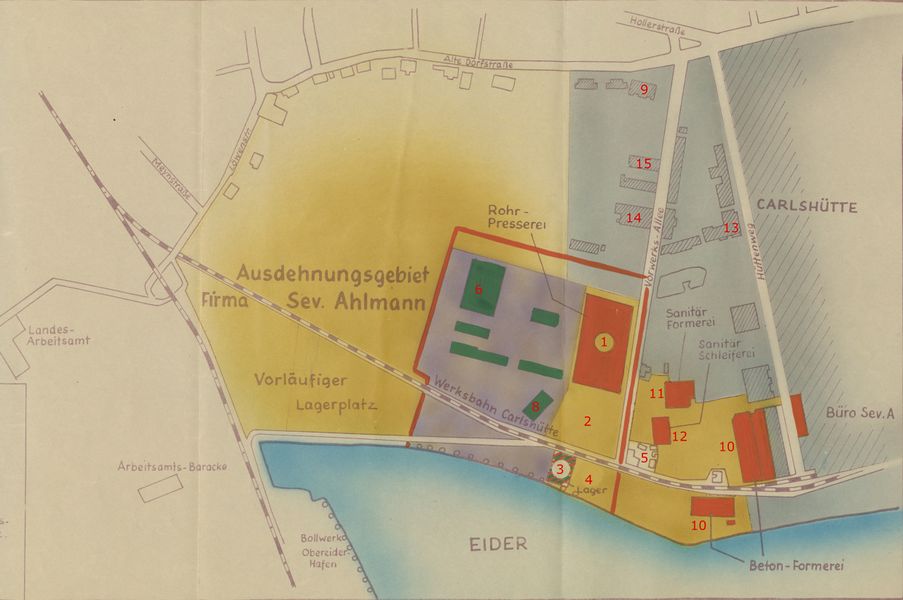
Datei:Fertig überarbeitet 1.1.A 00504 19510310 Produktionsgelände,043.jpg|Plan on which - in yellow - the expansion of the young company SAB is clearly visible. Outlined in red is the square that is the subject of the trade between the timber merchant Timm and the town. Yellow is the company Severin Ahlmann and purple is the company H.F. Timm. The buildings in detail: 1) Pipe pressing plant, 2) Severin Ahlmann storage yard, 3) Severin Ahlmann storage yard, 4) Severin Ahlmann storage yard, 5) Carlshütte residential building, now Vorwerk office, 6) Thormann hall (built in 1890), 7) Severin Ahlmann office in the Carlshütte, 8) Horse-keeping yard (ca. 1784), 9) Director's house, 10) Concrete moulding, 11) Sanitary moulding, 12) Sanitary grinding, 13) Haus & Hof Ahlmann, 14) Wagenremise (built in 1913), 15) Alte Meierei. | |||
<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
In the spring of 1951, Severin Ahlmann entered into negotiations with the town of Rendsburg to buy the Timm site – the entire plot, not just the subleased part. In the cover letter, the entrepreneur cites SAB's success story and "great initiative". He also emphasised the future importance of the company for the city and the Rendsburg economic area: greater turnover, more jobs, and higher tax payments could only be generated on the basis of the planned expansion. | |||
In March 1952, the efforts were crowned with success: the town sold Severin Ahlmann a total of four parcels of land totalling 4.3 hectares for DM 350,000. Of this, DM 80,000 for the actual plot of land, and DM 260,000 for various buildings, and DM 10,000 costs for miscellaneous inventory. The existing buildings also included the "Thormannhalle". | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 600 px> | |||
Datei:Lageplan Final.jpg|<br>Aerial view of the Carlshütte and SAB site, 1950s: 1 Director's house, 2 Old dairy, 3 Stables (built in its first form in approx. 1784), 4 Residence, later new Vorwerk office, 5 Carlshütte main office building, 6 Ahlmann house & farm, 7 Coach house (built 1913), 8 Thormann Hall (built 1890), 9 the Carlshütte. | |||
<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The first Ahlmann swivel bucket loader 1952/53 == | |||
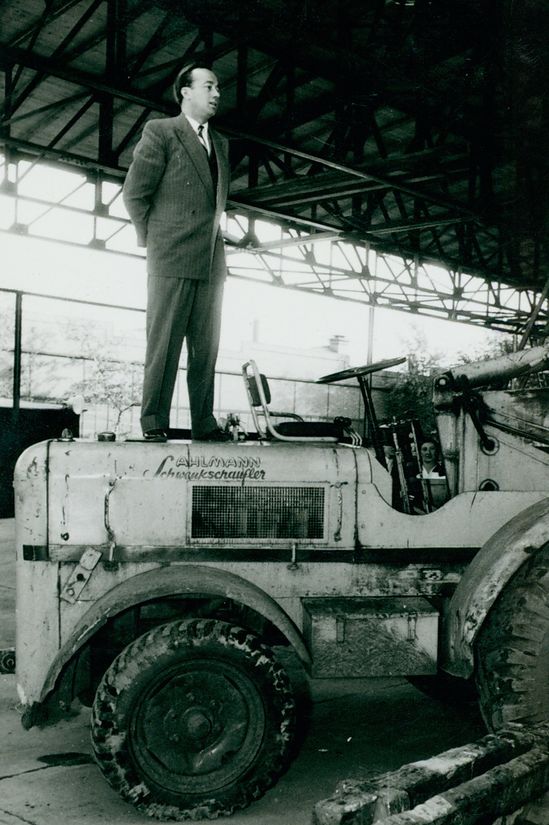
[[Datei:JSA Paul Bachmann April 1953 aus Schönrock.png|350px|thumb|right|Severin Ahlmann (left) and Paul Bachmann, responsible for sales of the bucket loaders, at the Hannover Fair in April 1953, with one of the prototypes of the then still called "Ahlmann all round" bucket loader.]] | |||
Intra-plant transport at both the Carlshütte and SAB was to be rationalised. Severin Ahlmann undertook trips to the USA with Carlshütte executives, such as the authorised signatory Friedrich Sensen, and the foundry manager Hans Schlothfeldt, to look into the rational organisation of work processes there. The team became aware of forklift trucks and bucket loaders, some of which were purchased from the importer Stinnes, and used from March 1952. | |||
The staff were sceptical at first: it was not uncommon to hear "Smiet dat Ding in de Eider!" “Chuck that thing in the Eider!”, when the forklift got stuck on the roads, which, at that time, were not very suitable for vehicles of this kind. But that soon changed to "Where's the forklift?" – so two more pieces of equipment had to be purchased. | |||
< | The idea arose to manufacture bucket loaders at the Carlshütte. One background to the initiative is that the first dead iron from the cupola furnaces could be put to use as the counterweight. It was Hans-Julius who had the initial idea. | ||
[[ | |||
</ | Severin Ahlmann now devoted more time to this topic, especially as his authorised signatory Paul Meyer at SAB relieved him of some of the day-to-day management work. In spring 1952, he entrusted the young commercial employee Rolf Schönrock with a market survey, which turned out to be promising. Severin called together a core team for the bucket loader project. It consisted of the naval architect Hans Boll, who had already proved himself in the construction of the Ahlmann ships COLONIA and CIANDRA, the mechanical engineer Mr. Hoffmann, the driver of the shovel loader at the Carlshütte Mr. Reimers, and finally Rolf Schönrock. | ||
In November 1952, the team travelled to Sweden to inspect the all-round bucket loader made by LECAB. This had a bucket that could be swivelled to both sides. Based on the LECAB shovel, three prototypes of their own Ahlmann swivel bucket loader were to be manufactured by the next industrial fair in Hannover in 1953. An ambitious goal, which was achieved despite some setbacks and internal resistance. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 550 px> | |||
Datei:1955 06 16 Richtfest Schwenkschauflerhalle 3.jpg|<br>Topping-out ceremony for the swivel bucket loader factory building at the Carlshütte in June 1955: Severin Ahlmann addressing the employees. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:19 GlückAuf Juni 1955 thump 1.jpg|<br>Glück auf", the Carlshütte employee magazine, reported in detail on the trade fair presentation of the swivel bucket loader in June 1955.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
However, the trade fair was not without its mishaps: during the demonstration for a Swiss quarry owner, an hydraulic hose burst. Schönrock quickly distracted the audience, as he himself reported, with "delicacies and alcoholic beverages". Business was done. They generally succeeded in gaining the interest of the public. The first small series production started. The Ahlmann swivel bucket loader began its triumphal procession, and became a synonym for entrepreneurial action, willingness to take risks, the will to diversify, and organisational skills. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== AHLMOPLAST - the beginnings of plastics production == | |||
Entrepreneurial creativity was also evident when venturing into a completely new material, as was previously the case when the Carlshütte started producing concrete. In 1953, Käte and Severin Ahlmann founded AHLMOPLAST GmbH & Co. KG, which marked the beginning of plastics production in the ACO-Carlshütten cosmos. | |||
It all started with the idea of using glass-fibre reinforced polyester instead of cast iron for the production of bathtubs. However, market demand specifically for bathtubs was still low, so a number of other products were manufactured with the material. These included underwater massage tubs, and modern chairs in the typical style of the time – reminiscent of the designs of Charles and Ray Eames. Light, comfortable and shapely, the seat shells were available in many different colours. | |||
A large order came from the Shell petroleum company: in 1956, the company’s iconic shell emblem made of AHLMOPLAST was presented for the first time. The illuminated logo consisted of two AHLMOPLAST shells illuminated from the inside. Gradually, all large Shell petrol stations were fitted with AHLMOPLAST shells. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 350 px> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00000 1957NNNN ACH,001.jpg|<br> The popular seat shells made of AHLMOPLAST, here in the breakfast room of the swivel bucket loader workshop at the Carlshütte. Even today, Ahlmoplast chairs can be found sporadically in Rendsburg and the surrounding area. <br> <br> . | |||
Datei:Unterwassermassagebehälter Glück Auf Februar 1957.jpg|<br> <br>An underwater massage tub made of Ahlmoplast. <br> | |||
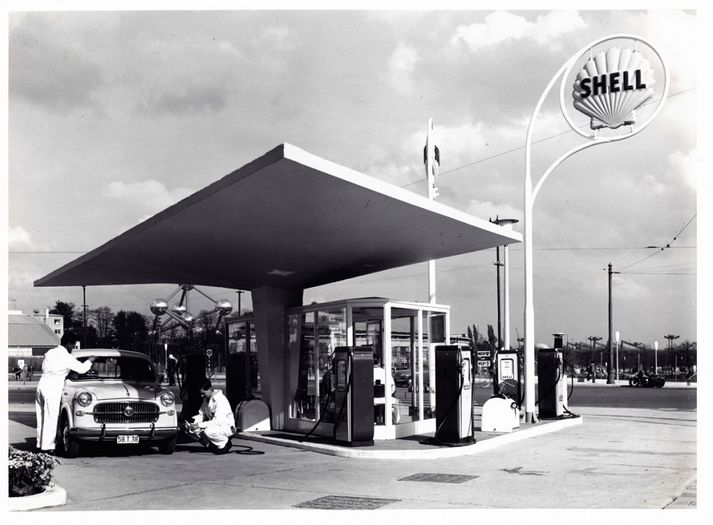
Datei:Schell-Muschel-Tankstelle.jpg|<br> <br>A Shell petrol station in the 1950s: The iconic shell is also made of Ahlmoplast. | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
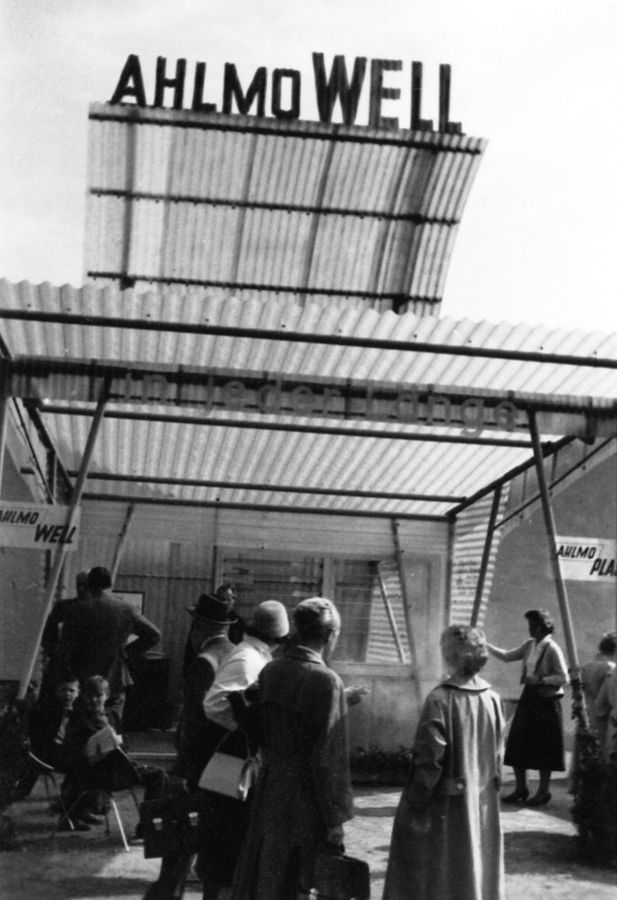
== AHLMOWELL from Andernach == | |||
Plastic production was also started in Andernach. The company produced sheets marketed under the brand name AHLMOWELL, later ACOWELL. As far as is known, this was the first time that the later company abbreviation ACO appears in the form of a brand name. | |||
The AHLMOWELL polyester corrugated sheets produced in Andernach were presented for the first time at the Berlin Industrial Fair in September 1956. They could be produced in many colours, and transparent or opaque, using a manufacturing process developed in-house. They could be used in a variety of ways, e.g., as terrace roofing, windbreaks, or for covered parking areas. For example, they could be found in Rendsburg's open-air swimming pool: a light band made of yellow AHLMOWELL adorned the outdoor pool. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 600 px> | |||
Datei:1.1.B 00122 1956 Industrie Ausstellung Berlin, 058.jpg|<br>AHLMOWELL at the 1956 industrial exhibition in Berlin. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:ACOWell Anzeige.jpg|<br> Contemporary print advertising for the ACOWELL GRP light panels. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 300 px> | |||
Datei:Ahlmoplast Plakat Kunststoffe.jpg|<br>Plastic products from Rendsburg and Andernach: AHLMOPLAST and AHLMOWELL. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 01051 1968NNNN USABersch,051.jpg|<br>A light strip made of yellow AHLMOWELL. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
[[Datei:Ahlmann Betonfenster.jpg|350px|thumb|right|At the Hannover Fair in 1955, Severin Ahlmann advertised the concrete windows with a stand that is visible from far and wide.]] | |||
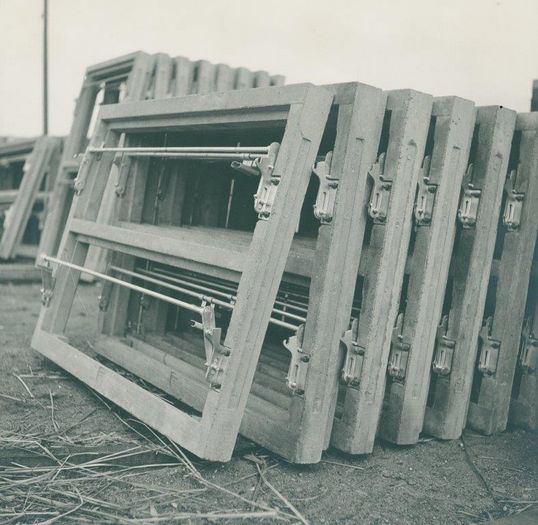
== The beginnings of concrete window production == | |||
In March 1954, SAB closed a licence agreement for the production of concrete window frames with the Hans Bördlein company, a concrete goods factory located in Reith in Unterfranken, Germany. The windows were intended for building construction, mainly for use in agricultural buildings. At the same time, the company developed its own concrete window construction facilities in Rendsburg for industrial and agricultural buildings, as well as for basements in residential buildings. Over the course of 1956, SAB Büdelsdorf began to produce windows according to its own designs. The licence was soon no longer required. | |||
The decision to enter the window manufacturing business proved to be ground-breaking. The production of concrete windows became the company's "bread and butter business" for more than 30 years. Sales volumes were high, and so were the margins. | |||
It was the far-sighted first SAB managing director Paul Meyer who pushed for this new business field. Years later, Severin Ahlmann wrote to him gratefully: "I often look back on the really great decision years ago to include concrete windows in the manufacturing programme. With the SAB proposal at the time, you made a leap in development possible that was of particular importance to us considering our dependency at the Carlshütte on the somewhat unstable cast-iron washing facilities market." | |||
Concrete window construction opened up a line of continuity that is still alive at ACO today with the plastic window segment. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 350 px> | |||
Datei:1.1.B 00442 1956NNNN ObjektfotosBetonfenster,004.jpg|<br> | |||
Datei:1.1.B 00442 1956NNNN ObjektfotosBetonfenster,006.jpg|<br> | |||
<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The SAB (ACO) product portfolio in the 1950s == | |||
In the mid-1950s, SAB's portfolio comprised three main product segments: the pure concrete products, the sanitary articles made of artificial stone, and the concrete frame windows. | |||
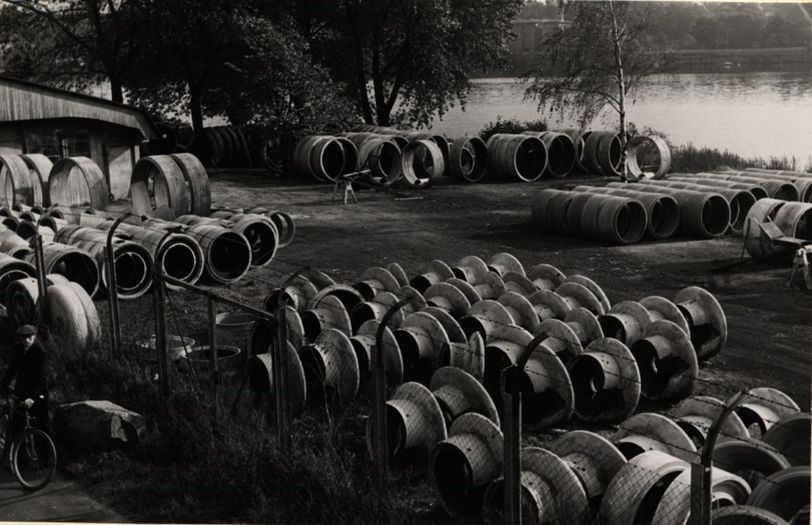
The start with roof tiles, feeding troughs and simple concrete slabs at the end of 1946 was quickly followed by the production of heavy concrete pipes for water management. Even now, they still make up the majority of SAB's concrete products. Rugged pipes ranging from filigree 100 millimetres to massive 1,000 millimetres in diameter are cast as moulded parts. They are mainly used in sewer construction, or for simple water conduits and house connections, and manholes. There are even manhole rings with diameters of up to two metres for this purpose in the range. Cast-concrete road gullies, kerbstones and pavement slabs are used in road construction. In 1954, the signs pointed to an expansion of production: investments were made in an automatic high-performance press for pavement and floor slabs. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 250 px> | |||
Datei:02 -1.1.B-00057 NNNNNNNN Hornemann,06.jpg|<br>Production of paving slabs on modern mixing and pressing equipment. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:1.1.B_00043_NNNNNNNN_Roehrenproduktion_1960er_03.jpg|<br>Kerbstone production. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:01 1950er Produktion 10.jpg|<br>Medium-diameter civil engineering pipes set up for drying. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
For building construction, SAB produced prefabricated parts made of reinforced concrete and artificial stone. These included staircases - as individual steps or complete systems - frames for doors and windows for installation in the façade, as well as window sills. These articles were mainly used in social housing construction. For example, large apartment buildings in Kiel-Wellingdorf were equipped with ready-to-install structural engineering products. | |||
In addition to the series, SAB also produced tailormade items for the construction industry. For bridge construction, for example, these included cover plates made of reinforced concrete, and sleepers. The construction of district heating pipelines required precast ducts. SAB engineers developed customised solutions for such projects. | |||
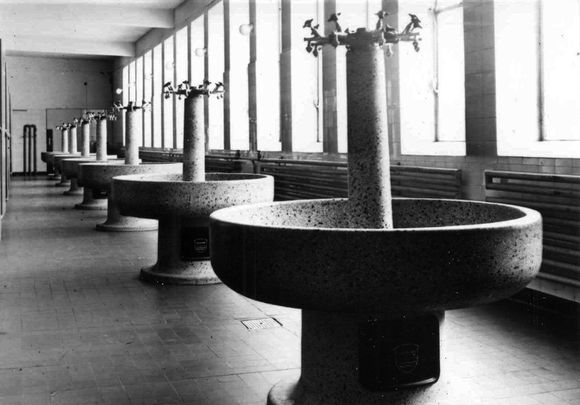
An example of artificial stone is marble granules. It differs from heavy concrete in the quality and grain fraction of the gravel mix and the aggregates. Grinding and polishing the moulded parts produces an outstanding appearance and attractive surface properties. Sanitary objects primarily involved large washbasins, circular washing fountains or channels. Also sink outlets, rinsing and washing tubs, and foot and shower tubs. Specialities are worktops for ice cream parlours. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 260 px> | |||
Datei:03 1950 Produktion 3.jpg|<br>Grinding the well-known "Venetia" ice-cream slabs, around 1950. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:04 15 GlückAuf Ostern 1954-002 - Kopie.jpg|<br>Winding staircase made of marble granules. A similar staircase is located in the garden house on the grounds of the Carlshütte. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
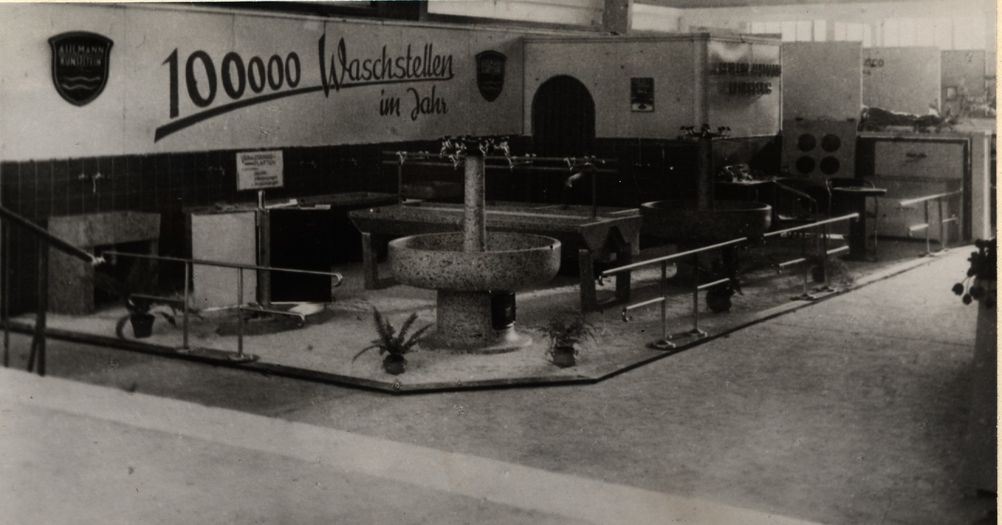
The counterparts to the SAB sanitaryware made of marble granules were provided by the Carlshütte and Ahlmann & Co. Andernach with enamelled cast iron products. The product portfolio of Carlshütte and Ahlmann & Co. Andernach went beyond this. All in all, the three Ahlmann companies offered a diversified range of sanitary and household products. In the 1950s, these could be recognised as branded products because they used the same labels. The products were also presented in a joint catalogue. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 300 px> | |||
Datei:05 1.1.A 00579 Katalog (evl zu Marmorkorn)-077 - Kopie.jpg|<br>Large washing system as in the form of troughs made of marble granules. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00579 Katalog S76.jpg|<br>Round washing facility made of marble granules. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:06 1.1.A 00579 Katalog (evl zu Marmorkorn)-078 - Kopie.jpg|<br>Basin and tub designs made of marble granules.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 350 px> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00504 19510310 Produktionsgelände 12.jpg|<br>SAB, Carlshütte and Ahlmann & Co. in Andernach jointly built up to 100,000 washing units within one year in the 1950s. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Family changes == | |||
The Hannover Fair of 1955 was of decisive importance, not only for the success of the swivel bucket loader, but also for the further development of Ahlmann's enterprises. The lady who directed the swivel bucket loader from the upper floor of the trade fair pavilion with her pleasant voice was Maria Jänicke. She was the daughter of a publisher. Josef-Severin Ahlmann fell in love with the attractive and polyglot woman. She became his new partner. In provincial Büdelsdorf, this vision soon caused quite a stir. | |||
Only a few weeks after this encounter - in June 1955 - Severin Ahlmann had a conversation with his mother Käte about the future of the Carlshütte. He probably did not choose his words very carefully, because Käte took it to mean that her son wanted to force her out of the management of the company. She suspected that the initiative for this came not from him but from his new partner. Her relationship with Maria was not on the best footing anyway. | |||
A quarrel ensued, which escalated in February 1956. Käte Ahlmann rescinded the general power of attorney for the Carlshütte granted to her son. Cooperation no longer seemed possible. | |||
In the autumn, Käte proposed a split to her son: Severin should receive the subsidiary in Andernach in exchange for his shares in the Carlshütte. Severin's nephew, the four-year-old Hans-Julius, was now intended as the prospective main heir to the Carlshütte. SAB (ACO) remained unaffected by this arrangement, i.e., continued to be owned by Severin Ahlmann. Severin agreed to the split with a heavy heart. | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 900 px> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00538 Presseclipping 1960er-1980er,10.jpg|<br>The editorial article by Severin Ahlmann, which was placed in the press several years after the split, shows how important it was for him to establish an independent identity. Independence is emphasised. The words also make clear how painful the move was for him. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
= Between Rendsburg and Andernach 1957 to 1968 = | |||
== Reorganisation of the companies == | |||
[[Datei:JSA und Maria Ahlmann 1964 aus Schönrock S43.jpg|400px|thumb|right|Josef-Severin Ahlmann with his second wife Maria, née Jänicke, 1964.]] | |||
In spring 1957, the family's companies were reorganised according to Käte Ahlmann's proposal. A contract was signed, dated 4 March. | |||
Severin now had three independent companies: Ahlmann & Co. in Andernach, with its focus on cast iron products, SAB in Büdelsdorf for concrete products, and Ahlmoplast GmbH, with its plastic products. | |||
In December of the same year, Severin and Maria Jänicke married in Munich. The couple moved their centre of life to Andernach. In nearby Bad Breisig, they had a house built by architect Paul Wittig. | |||
Paul Meyer's importance in the management of SAB now increased even more, as its owner was rarely seen in Büdelsdorf. This spatial separation between Severin Ahlmann and the place of his birth remained unchanged until his death. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The Ahlmann sketchbook 1957 == | |||
The ACO archive includes a unique testimony, the so-called Ahlmann Sketchbook from 1957. It gives an overview of Ahlmann's undertakings at that time in a concise and visually appealing manner. Among other things, it explains how a cast-iron bathtub is made, and how it reaches the customer, the development of the swing bucket loader is shown, as well as the rich portfolio of stoves, concrete windows and plastic products. | |||
Probably this prototype company brochure was never published in this form, as the joint Ahlmann company no longer existed after the split between Severin and his mother Käte Ahlmann. | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 320 px> | |||
Datei:IMG 2070.JPG|<br>Overview of production in Andernach at the time of the separation of the companies: page from the Ahlmann sketchbook 1957.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:IMG 2071.JPG|<br>The illustration of the production of SAB, page from the Ahlmann sketchbook 1957. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Developments in Andernach == | |||
In 1957, Severin Ahlmann and his former co-partner Hans Günter Möller also went their separate ways at AHLMOPLAST. On 30 May 1957, Severin Ahlmann completely took over the company, which had emerged from the plastics division of the Carlshütte. He moved the company headquarters to Andernach. | |||
In Andernach, the plastics division continued to develop very well. At home, the sheets called AHLMOWELL were supplied to building material wholesalers through a network of agents in Germany. Abroad however - instead of exporting the products - the AHLMOPLAST machines required for production, were sold to licensees, together with the necessary know-how for production. | |||
Already in autumn 1958, Severin Ahlmann could move into his new office in Andernach. The spacious new administration building was an impressive advertisement for the polyester light panels produced at the plant, which were installed in the façade. The new building replaced the temporary offices housed in former military barracks. Three ACO covered car parks made of ACOwell were also built around the building. | |||
Rolf Schönrock left the Carlshütte and, after a brief interlude at another company in Berlin, followed Severin Ahlmann to Andernach. He was entrusted with the expansion of the plastics business in Andernach in 1958. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== AHLMOPLAST worldwide: Export of plastics know-how == | |||
For the distribution of the AHLMOPLAST systems, Schönrock and a patent attorney developed licence agreements, and he had design documents produced which were to be made available to future licensees for repair and maintenance, and he got to know the market and customers. | |||
The acquisition of licensees was initially concentrated on other European countries. Various building material manufacturers were approached, especially manufacturers of asbestos cement, corrugated sheet metal and corrugated aluminium. The contacts to the ETERNIT Group were important here. After presentation trips in Yugoslavia and Japan, the first contracts were signed at the end of 1959. Especially the trip to Japan was an outstanding experience for Rolf Schönrock. He admired the traditions, and was fascinated by the tremendous modernisation of the country. | |||
[[Datei:Tempura Dinner aus Schönrock neu.png|400px|thumb|right|Japan-Reise 1959: Trip to Japan in 1959: Rolf Schönrock at a traditional tempura dinner.]] | |||
The final breakthrough for the distribution of AHLMOPLAST machines came in 1960. Further licence agreements were closed with ETERNIT companies in Norway, Denmark, Sweden, Belgium, France, Great Britain and South Africa. In addition, ASSMANN, a metal and plastics processing company in Graz, acquired a plant. | |||
In autumn 1960, Schönrock flew to Moscow with the technical manager of the Andernach plant, Karl Pulch. Behind the Iron Curtain, too, people began to take an interest in AHLMOPLAST. However, the trip did not lead to a business deal – but at least there was plenty of Crimean sparkling wine and caviar. | |||
In 1961, after a return visit by the Japanese to Andernach, a contract was signed. In the same year, two more production lines were sold to Japan. Licence agreements were also signed with customers in Australia, South Africa and New Zealand - following another trip by Schönrock. | |||
To enable the exchange of experience with the first customers, Severin Ahlmann sent out invitations to the first AHLMOPLAST conference scheduled for 17/18 October 1960. In technical presentations, the attendees gained valuable insights and ideas on the raw materials, the production and the application areas of the products. | |||
[[Datei:Assmann_bei_Ahlmoplast-Konferernz_aus_Schönrock.jpg|400px|thumb|right|Participants at the first AHLMOPLAST conference in 1960: Left row: Mr Lippert, Mr Assmann, Mr Johnsen, Mr Beck-Bang, middle row: Messieurs Evard, McEvilly, van der Stichelen-Rogiers, van den Bost; right row: Mr Wibelund, Mr Malling, Mr Tischbein.]] | |||
The format proved so successful, that another, now much larger conference was held in autumn 1962. | |||
[[Datei:Ahlmoplast Konferenz 1962 aus Schönrock.jpg|650px|thumb|center|Impressions of the second AHLMOPLAST conference in 1962 in Andernach.]] | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Acquisition of Bördlein, and establishment of the new site in Reith == | |||
[[Datei:Reith ex-Bördlein um1960.jpg|400px|thumb|right|Barely recognisable as a company: around 1960, Bördlein in Reith still had far from adequate production conditions. Modernisation and expansion only set in after the takeover by Severin Ahlmann.]] | |||
In the course of 1959, Severin Ahlmann acquired the Hans Bördlein concrete products factory in Reith, Unterfranken. The licences for the concrete-framed windows, which had been produced in Rendsburg for five years, came from this company. | |||
Paul Meyer is the driving force behind the takeover of the former licensor. The window business was going well, and was to be further expanded with the new acquisition. From Reith, SAB could also open up new sales markets in southern Germany. | |||
Concrete windows were now manufactured at two locations, while sales were managed centrally from Büdelsdorf. Reith can be regarded as the first location of the later ACO company outside Rendsburg, as Ahlmann & Co. in Andernach was independent and had other production focuses. | |||
[[Datei:Anmeldung Reith.jpg|600px|thumb|center|The business registration for Reith.]] | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Success in Reith == | |||
[[Datei:1.1.B 00064 1962NNNN Objektfotos Betonfenster,05.jpg|400px|thumb|right|Ahlmann concrete windows on a simple-looking open-air exhibition stand. The simplicity is deceptive - in fact, concrete windows were the cash cow of the 1960s.]] | |||
"Install AHLMANN concrete windows ... and never worry about it again." Not only this advertising slogan, but also the products were convincing. From the beginning, the turnover increased continuously, and soon 150,000 units were sold per year. The return was enormous, and the highest of all the product segments in the company. By way of comparison: the processing of 1 kilogramme of window concrete brought in about 90 pfennigs, whereas the processing of 1 kilogramme of heavy concrete for civil engineering in Rendsburg only brought in about 4 to 6 pfennigs. | |||
The new acquisition was the starting point of the strong expansion in this decade: in terms of sales areas, product range and turnover. | |||
Thus it was window production that created the financial basis for Severin Ahlmann's success in the 1960s. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Change of managing director after Paul Meyer's death in 1962 == | |||
[[Datei:1.1.A 01052 1957NNNN PaulMeyer,030 todeanzeige Severin.jpg|400px|thumb|right|Paul Meyer's obituary.]] | |||
In Rendsburg, Paul Meyer unexpectedly suffered a heart attack in April 1962 and died, not yet 60 years of age. The experienced managing director was not only the creative heart of SAB from the beginning, he was also a friend of the Ahlmann family. His widow, a sister of Friedrich Sensen, one of the directors of the Carlshütte, was initially able to stay on in the house built especially for the Meyer family on the company premises. | |||
In the dynamic phase experienced by the company at that time, a change of managing director was certainly not beneficial. To avoid a management vacuum after Meyer, Rolf Schönrock took over the management in Rendsburg on an interim basis from January 1963. Together with the Rendsburg management, Schönrock was able to secure the positive turnover and profit situation. In March 1964, he returned to Andernach, as he had long been earmarked to take over the management there. | |||
In January 1964, Heinz Rother succeeded him in Rendsburg. His work for ACO, however, remained a relatively brief intermezzo. He was succeeded by Rudolf Kobelt, the former sales representative for concrete windows. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 270 px> | |||
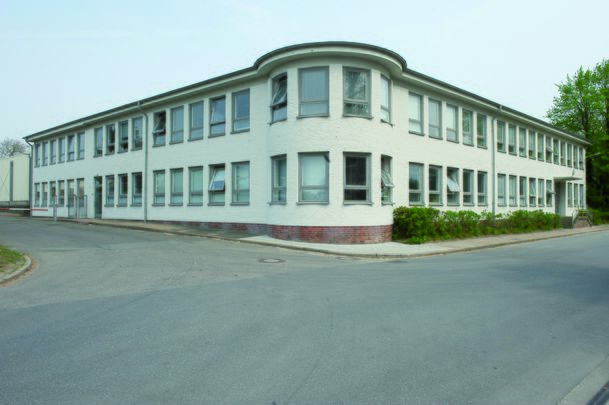
Datei:1950er_Verladung_von_Rohrsegmenten_2.jpg|<br> Loading raw segments at SAB in the 1950s. In the background is the historic residence with its characteristic rounded shape. The Vorwerk office was built on this site at the beginning of the 1960s. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:Buero Vorwerk Aussenansicht.jpg|<br> The so-called Vorwerk office, on the SAB site, which was first occupied in 1962. With its curved outlines, the building reflects the shape of the previous building on the same site. The name Vorwerk refers to the Vorwerk estate on the banks of the Eider – the former farm attached to the old Rendsburg fortress. <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
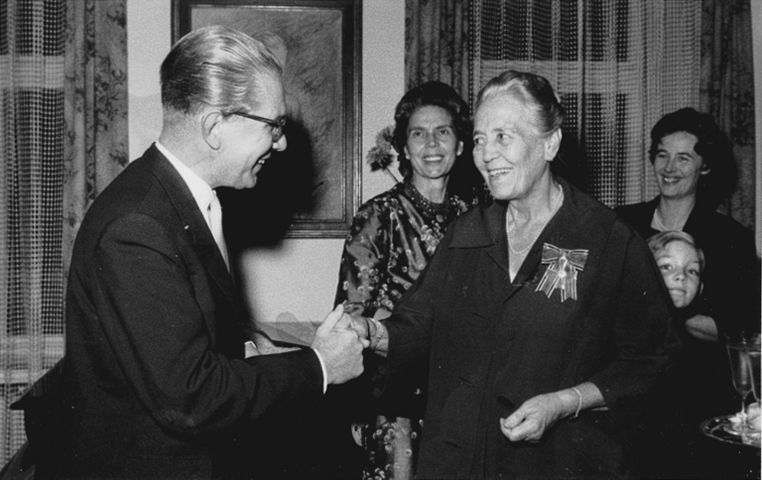
== Käte Ahlmann's death in 1963 - the end of an era at the Carlshütte == | |||
On 5 June 1963, Käte Ahlmann said goodbye to her grandson and prospective successor, the now eleven-year-old Hans-Julius, at Hamburg Central Station. She traveled to Innsbruck to undergo extensive treatment at the clinic of her son-in-law Prof. Max-Joseph Halhuber. Her heart was weakened. Käte Ahlmann's health had deteriorated more and more over the preceding years, not least because the restless entrepreneur did not take it easy. The treatment was ineffective. Only ten days later, on 15 June 1963, she died in Innsbruck. | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 320 px> | |||
Datei:Minsterpraesident_SH_von-Hassel_KA_6_18.jpg|<br>Käte Ahlmann with the Minister President of Schleswig-Holstein, Kai-Uwe von Hadsel, at the award of the Grand Cross of Merit of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany on 3 October 1960. The picture also shows Dr Marlene Halhuber-Ahlmann; Juliane, now Jebsen; and her son Hans-Julius. Kai-Uwe von Hadsel's connections to the Ahlmann story were manifold. His grandmother was a Thormann, so he came from the family that once owned part of the ACO site. He was also an uncle of Hans-Michael Jebsen, Hans-Julius Ahlmann's half-brother.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:Letzter Weg aus Trauerschrift Käte Ahlmann Sommer 1963.jpg|<br>Funeral procession for Käte Ahlmann on 21 June 1963 on the Carlshütte site. Eleven-year-old Hans-Julius Ahlmann carries the cushion with the deceased's Federal Cross of Merit. The 3,000 employees of the Carlshütte form a guard of honour. Their long-time confidant Dr Carl Wuppermann speaks at the funeral service. The shadow on the right is cast by the transformer building; the old "sheet metal building" can be seen on the left.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
This was not only the end of an era for Carlshütte. The future was also uncertain. In the Christmas edition of the Foundry magazine "Glück auf", published in December 1963 (the first after Käte's death) her daughter Marlene Halhuber-Ahlmann, who now, commuting between Innsbruck and Büdelsdorf, administered the legacy, wrote: "Everyone belonging to the community of foundry people shares our sense of responsibility. Trust me that I take my part as seriously as my mother did, and that I am even more in need of your support!" | |||
{{#evu:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tdQoWI4Ni8Q | |||
|alignment=center | |||
|description=What was it like at the Carlshütte and the neighbouring company of Severin Ahlmann during this period? An NDR documentary about the Kiel Canal, made the year after Käte Ahlmann's death, shows impressive images. Scroll directly to minute 11:54 to see pictures of the Carlshütte, to minute 15:16 to see pictures of Severin Ahlmann's concrete production.}} | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The development of cast iron production in Andernach == | |||
Cast iron bathtubs remained the most important line of business in Andernach. In 1956, turnover in cast iron bathtubs was DM 10 million, and apart from minor setbacks, it rose steadily over the next few years. In 1968, it amounted to DM 18.2 million. By contrast, turnover in plastic products peaked in 1962 at DM 10.5 million, after which it declined with certain fluctuations. | |||
In 1961, the former foundry manager at the Carlshütte, engineer Karl Pulch, took over the technical management in Andernach. Under his leadership, the automatic enamelling machine was developed in 1962. This technical innovation eased the heavy physical work involved in enamelling the tanks by means of a semi-automatic spreading device with a compressed air sieve. Despite the innovation, and the resulting labour savings, attempts to sell the automatic strewing device abroad failed. In the end, the innovation was only used in the company's own operations. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 300 px> | |||
Datei:Gießerei 2 ACO Unternehmensbroschüre 1974.jpg|<br>Hard work on the cupola and electric ovens. ACO Andernach saw itself as the most modern plant for the production of bathtubs in Europe.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:Gießerei 1 ACO Unternehmensbroschüre 1974.jpg|<br>Automatic moulding and casting machines for bathtubs, and later also for boilers and customised castings, have been in use at ACO Andernach since 1964. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
A few years later, the Carlshütte in turn succeeded in developing an electronically controlled, fully automatic enamelling machine that again reduced the use of personnel for this hard work. Apparently, ACO Andernach and the Carlshütte were engaged in an innovation competition. | |||
The automatic bathtub moulding machine introduced in 1963, on the other hand, proved to be a successful model. In October 1964, ACO Andernach invited the entire German and nearby European wholesale trade to visit the factory. | |||
Over the years, ACO Andernach increased its share of the domestic market, and finally became the market leader for cast iron bathtubs from 1966. Andernach was the first plant to switch completely to titanium enamel, which made a significant contribution to its success. The production facilities for shower trays were also expanded. This investment was completed in 1966, and consolidated the company's pre-eminence in the sanitary sector. | |||
A smaller area of business at the Andernach plant was customised casting, but this remained comparatively small. | |||
At the end of the 1960s, the system of independent sales representatives was disbanded and replaced by ACO sales offices with permanently employed sales staff. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Windows, honeycombs, heavy concrete: Products from Severin Ahlmann Rendsburg in the 1960s == | |||
For the Rendsburg site, window production was the most profitable business segment. The product portfolio now included system concrete windows for commercial buildings. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 380 px> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00581 SAB Preisliste 1960.tif|<br>The price lists from 1960 and 1964 show the company's portfolio, and the company's best-seller in the 1960s.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00581 Betonfenster Preisliste 1964.jpg|<br>The use of the SAB lettering is remarkable, because the company was already renamed "Severin Ahlmann" in 1951. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
The honeycomb windows made of concrete were a special design. Honeycomb windows were reinforced, window fronts with narrow-profiles used in prefabricated construction. They were statically safe, weather-resistant, and required no maintenance. Here, too, the slogan applies: "Install and never worry about it again!" The range was primarily aimed at the industrial sector, and was used, for example, in factories or in the properties of the German armed forces. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 300 px> | |||
Datei:1.1.B 00064 Lagerhalle Mercedes und Auto Union um 1960 Ausschnitt.jpg|<br>A typical example of the use of honeycomb windows in industry: a factory for Mercedes Benz and Auto Union, before the sale of the latter brand to VW in 1964/65. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:1960um_Ahlmann_Wabenfenster_Werkhalle_Ringsdorff-Werke_GmbH_Bad_Godesberg-Mehlem.jpg|<br>Ahlmann honeycomb windows in a factory at the Ringsdorff-Werke in Bad Godesberg-Mehlem, one of the world's leading manufacturers of carbon brushes, 1960s.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:1.1.B 00063 1962 Neubau erstes Bürogebäude, 002.jpg|<br>Honeycomb windows from ACO were of course also used in the new construction of the Vorwerk administration building, seen here in the stairwell.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
Another special form was widely used: decorative bricks. They were available in trapezoidal, conical or circular shapes, and were used as façade cladding, or to create ornamental light walls, or as decorative elements for staircases, connecting walls and other representative spaces. They could be glazed or unglazed. Architects were enthusiastic about the diverse design possibilities of decorative stones. Decorative stones were often used in religious buildings. In the course of the 1960s, they became a defining element of contemporary architecture. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 400 px> | |||
Datei:CAU Kiel.jpg|<br>A look inside the Kiel University Church reveals the play of colours of the more than 2,000 glazed ACO decorative stones.(image source: sh-Kunst.de) | |||
<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
{{#evu:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DYjtUFfvt4k | |||
|alignment=center | |||
|description=In 1960, ACO was hesitant to supply the world-famous Kaiser Wilhelm Memorial Church. It seemed too big a risk because the honeycombs contained steel wire. This could have rusted and caused parts of the façade to crumble. ACO did not want to be responsible for this damage. The contract therefore went to a competitor. | |||
But a few years later, ACO did take on a church project that was not necessarily smaller: the church of the Christian Albrechts University in Kiel, now a listed building, with its strikingly colourful windows. We tracked down the architect from back then, Ekhart Kettner, now 91 years old, and met him for an interview in the church. This interview produced really exciting insights that one could never get otherwise.}} | |||
In the middle of the decade, the product portfolio of the Rendsburg plant also included the traditional programme of heavy concrete production for the northern German region. Marble granule and artificial stone products were also still on the market. However, both took a back seat to the expanding concrete window business. | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 350 px> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00538 Presseclipping 1960er-1980er,01 bearbeit.jpg|<br>The SAB site in the 1960s. Where the concrete windows used to be mass-produced - in the Thormann hall - the public rehearsals of the festival orchestra and the concerts of the Schleswig-Holstein Music Festival take place today - especially in the summer months.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 500 px> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00531 19650703 Werbeanzeige,001.jpg|<br>Unusual in appearance and language: Severin Ahlmann's newspaper advertisements from the mid-1960s. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00538 Presseclipping 1960er-1980er,03 ganz.jpg|<br>Already present: the ACO logo, but at the time for Rendsburg still in a shade of blue. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
In 1966, the company employed about 200 people at its locations in Rendsburg and Reith, generating an annual turnover of about DM 10 million. The number of employees shows how high the proportion of manual work still was at this time. In the same year, Severin Ahlmann's plant in Andernach generated a turnover of DM 25.8 million with about 450 employees. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The first step abroad: Sales of concrete windows in Austria 1964 == | |||
After the production of concrete windows picked up strongly at the beginning of the 1960s, especially at the still young Reith site, Severin Ahlmann took a forward-looking step: for the first time, a concrete product was to be sold abroad. At the Munich exhibition of the German Agricultural Society in 1963, a special interest in Ahlmann's barn windows was observed among Austrian farmers. The decision was therefore made to supply the Austrian market with concrete windows as well. | |||
[[Datei:Anzeige ACO Landwirtschaft.jpg||300px|thumb|right|The agricultural sector had been an important sales area for Ahlmann's concrete windows from the very beginning. Especially in Austria, which was still heavily agricultural in the 1960s, the company therefore saw a lucrative sales market.]] | |||
A suitable distribution partner was found in Gebr. Assmann & Co. in Leibnitz, Styria. The cooperation was initiated at the beginning of 1964, when the current interim managing director, Rolf Schönrock, contacted the industrialist Dr. Emmerich Assmann. Assmann's Graz plant was already the licensee of an AHLMOPLAST plant. Now the business relationship was to be extended to the window sector. After the customs situation had been clarified, sales in Austria began in the middle of 1964. However, there were no explicit plans for a licence or own production in the neighbouring country. It was rather a question of utilising the capacity of the factory in Reith or expanding there. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 650 px> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00836 Assmann Schönrock 1964.pdf|<br>Letter from Rolf Schönrock to Emmerich Assmann, in which the first foreign distribution of a Rendsburg product was initiated in February 1964.<br> PLEASE CLICK TO READ BOTH PAGES! <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== 1965 First use of the ACO logo lettering for Rendsburg == | |||
The different names of the individual companies – Severin Ahlmann Rendsburg, Severin Ahlmann Reith, and Ahlmann & Co. Andernach – were confusing and unintuitive for the market. For this reason, the abbreviation ACO for Ahlmann & Co. Andernach was gradually introduced as the brand and logo for all three companies. ACO was to become an unmistakable brand with a strong recognition value. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 230 px> | |||
Datei:SAB Logo.jpg|<br>The old SAB lettering. The abbreviation stands for Severin Ahlmann Beton – the abbreviation was still in use in the 1960s, and had a certain popularity, although the name of the Rendsburg company had already been changed from Severin Ahlmann Beton to Severin Ahlmann, Rendsburg in 1951. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00538 Presseclipping 1960er-1980er,03.jpg|<br> During the 1960s, the abbreviation ACO also became common in Rendsburg, initially still in blue, and often with the small addition SAB.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[Datei:1.1.B 00064 1969 Norla.jpg|600px|thumb|center|In 1969, the company advertised its concrete windows and prefabricated garages at Norla in Rendsburg under the now familiar ACO abbreviation in red.]] | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The further development of plastics production at ACO Andernach == | |||
The 1960s were marked by a series of pioneering innovations in the plastics sector at ACO Andernach. In 1965, ACO was the first company on the German market to develop shower partitions, called ACO TRENN. The partitions made of shatterproof fibreglass were in line with the trend for more comfort in the bathroom. A significant increase in sales was achieved here, and by 1974, the company had a market share of 20 percent. | |||
The importance of plastics production was not limited to the Andernach plant. In 1968, process engineer Heinz Dieter Brink from ACO Rendsburg went to Andernach to familiarise himself with plastics. Here he got to know the corrugated polyester sheet production. The connections and communications between Rendsburg and Andernach were lively. Back in Rendsburg, he combined the core competence of concrete in Rendsburg with the plastics competence from Andernach. On this basis, something completely new and innovative was to be created in 1969: the first ACO channel made of polyester concrete. | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 500 px> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00167 1974NNNN ACOBroschüre,006.jpg|<br>ACO TRENN in a bright, modern design for more comfort in the bathroom. The rather revealing image appeared in a company brochure in 1974. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Experiments in the plastics sector == | |||
In 1958, the then managing director of Ahlmann & Co. Andernach, Mr. Simmat, proposed to produce plastic tiles according to the American model, and to establish them on the German market. The idea was based on the assumption that cumbersome tile removal during bathroom renovations could be avoided by using easy-to-glue plastic tiles. Production was started, and even a mail-order company for plastic articles was founded. Plastic tiles, however, do not go down well in Germany. Consumers stuck to ceramic tiles, and so production was eventually stopped. | |||
The attempt to manufacture sports boats from glass fibre-reinforced plastic, which began in 1966, was also unsuccessful. At the international boat show in Hamburg in 1967, a large houseboat, a sailing catamaran, an open motorboat, a fishing boat, a bathing island, and a jetty were presented. | |||
The idea sounded promising at first: the boats were supposed to be light and cheap to produce. However, the material turned out to be unsuitable. Mr Weber, Severin Ahlmann's driver, got into distress on a test trip, and involuntarily met seals on a sandbank off Sylt before he was rescued. The plastic boats did not have sufficient stability, and production was discontinued. Nevertheless, Severin Ahlmann was still convinced of this project later on. In his autobiography from 1999, he wrote that it was a big and expensive mistake to abandon the leisure catamarans. | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 320 px> | |||
Datei:Anzeige Badeinsel.jpg|<br>Advertising for ACO bathing islands...<br> <br> | |||
Datei:Anzeige Katamaran.jpg|<br>...and catamarans.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[Datei:1.1.A 00527 1967NNNN Katamarane,002.jpg|600px|thumb|center|The ACO houseboat at the international boat show in Hamburg.]] | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Start of garage production in Rendsburg in 1968 == | |||
The end of the 1960s saw a turning point at ACO: heavy concrete production for water management in the Schleswig-Holstein sales region was discontinued in 1968 for reasons of market policy and investment strategy. This marked the end of an important tradition in Rendsburg: the company's history began 20 years earlier with such slabs and pipes. | |||
[[Datei:1.1.A 00049 Anzeigen ACO Fertiggaragen,001 Ausschnitt.jpg|350px|thumb|right|"Protect what is beautiful!" Germany's favourite means of transport needed an appropriate shelter. The marketing at the time produced many a curiosity.]] | |||
At the same time, in spring 1968, Severin Ahlmann introduced a new product to the line of concrete articles: garages. Like the original window production in the mid-1950s, this product was not an in-house development by Ahlmann, but was licensed. The licensor of the garage production was J. Kaletka, Ing.-Büro für Bau- und Betriebsplanung, IBK for short, in Gaggenau, Baden. | |||
The concrete system garages were completely prefabricated in the factory, then transported to the customer by truck, and erected on site. These were really large items that ACO now delivered to the licence area, almost all of Schleswig-Holstein, initially with the exception of some regions north of Hamburg. | |||
Garage production flourished, and the product was given the name "ACO Stabil". The ACO garage quickly established itself as a pragmatic and cost-effective solution for parking cars. It was produced in Rendsburg for almost a decade. | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 500 px> | |||
Datei:Garage1.jpg|<br>Manufacturer's brand with serial number on a system garage, the so-called "ACO-Garage".<br> <br> | |||
Datei:Prospekt ACO Stabil.jpg|<br>Logistics and image of the product, 1970s brochure.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
= Launch and first successes of ACO Drain 1969 to 1974 = | |||
== ACO Drain: Idea and product == | |||
At the end of the 1960s, surface drainage was still mostly point-based. This involved draining from individual gullies by way of buried drainage pipes. According to this approach, the water had to reach the lowest points on the surface, which was why cross gradients were required over large areas. The new concept of linear drainage using long drainage channels was the much more elegant solution. | |||
[[Datei:Gefaellearten Auszug Fliesenleger-Handbuch.jpg|500px|thumb|left|Sketches of the two most common types of gradient. The simplicity of the gradient principle towards a straight line - the DRAIN channel - becomes clear.]] | |||
It was two independent sales representatives, Eberhard Grundmann and Fritz Fiedler, who approached the head of ACO Sales, Karl Arno Ebsen, with the idea of drainage channels. A new, innovative product idea was being sought, because at this time, window production had passed its zenith. A kick-start was given by the garage sector. Here the question arose of how best to realise the drainage in front of the prefabricated garages. | |||
Drainage channels were already available on the market. ANRIN, for example, produced a 1 m long asbestos cement channel made of pipe half-shells, with glued-on side walls made of asbestos sheets. Arno Ebsen approached ACO engineer Dieter Brink in Rendsburg. Brink developed the original idea further, for example, by turning the pipe half-shells into pipe third-shells, with glued-on side walls with a length of 1.2 m. | |||
[[Datei:DRAIN Asbest Konstruktion 1969-70.jpg|280px|thumb|right|Cross-section through the initial DRAIN construction of bonded fibre-cement segments.]] | |||
Severin Ahlmann had yet to be convinced. The failure of the catamarans still sat deep. After hesitating for a while, he gave the green light for the start of channel production. The innovation was introduced on 1 May 1969, already under the product name ACO DRAIN, which is still in use today. | |||
It quickly became clear that ACO channels were easier to handle than conventional channels: they did not require any formwork on site. In addition, the channel was lightweight. "The advantage of our channel lies in the special construction ... as well as in the low transport weight. Compared to conventional channels that are shuttered on site, our channel is cheaper because ... the channel does without," said Arno Ebsen. | |||
ACO DRAIN was a decisive turning point in the history of ACO. The product would shape the future direction of the company. In the following years, ACO developed from a building materials generalist with a focus on window production, into a specialist provider of drainage solutions. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 450 px> | |||
Datei:ACO Drain 1969,002.jpg|<br>Abb. The first brochures for ACO Drain in 1969. At the beginning, the main material was fibre cement, also known as asbestos cement or Eternit. The raw materials were pipes and sheets made of this material. They were supplied directly by a manufacturer in Bremen. In the cutting department at ACO, the asbestos pipes of 1.20 metres length were then cut with a milling machine. This produced one-third shells, which were glued to the cut panels on the long side, and fitted with the metal gratings on the open side in the same way. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:ACO Drain 1969, 001.jpg|<br> All in all, the production of the channels in the early days was still a long way from mechanical mass production: they were basically handcrafted products. "We are on the right track in terms of the system, but the concept, and the technology are not yet perfect," was Ebsen’s assessment. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Customers and first sales success == | |||
In principle, the drainage channels were aimed at the specialised building materials trade, as well as construction companies. Building authorities and industrial architects were also interested. | |||
It was understandable that special advertising efforts were being made with all planning authorities in mind, and that users and architects were also being addressed directly. Federal and state building authorities, as well as road construction authorities were sent brochures, as were mineral oil companies that build petrol stations. In addition, the car industry was addressed because it was involved in the planning of garages. | |||
In the year of the market launch, i.e., from May to December 1969, ACO achieved a turnover of DM 260,000 with the DRAIN channel. A phenomenal success! | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 500 px> | |||
Datei:Preisliste ACO Drain 1969.jpg|<br>Price list number 1 for ACO Drain. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:Marktplatzentwässerung Uelzen.jpg|<br>Hydraulic calculation for the drainage of the market square in Uelzen with ACO Drain, 1969. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Adjustments needed - new material, polymer concrete == | |||
[[Datei:Constructa 1970 Reklame.jpg|320px|thumb|right|Poster of the CONSTRUCTA building trade exhibition in Hannover in 1970, where ACO exhibited the fibre cement DRAIN channel. The innovative design was well received by the trade visitors.]] | |||
The response to the DRAIN channels at the Constructa building trade fair in Hannover at the end of January 1970, not to mention the sales to date, the results of market research, and the advertising channels that were used at the time, were certainly promising. But the first problems arose a few months after the start of production. The channel proved to be unstable. The Achilles' heel of the construction was the bonding. Adhesive surfaces that were too small, caused the frequent collapse of the gratings under load. In addition, fibre cement panels were inflexible when it came to forming. Thus, less than a year after the market launch of the channels, a change in the production process was on the horizon. Both the material and the forming were being optimised. Dieter Brink's team had a favourite as the new material: polymer concrete. This would make it possible to cast the channels in their entirety instead of gluing them together. | |||
ACO already had experience in the production of GRP moulds with a backfill of sand mixed with polyester resin, i.e., polyester concrete, because of the concrete honeycomb production using the vibro-pressing process. This was the area of expertise of the ACO model maker Gerd Grabow. Dieter Brink came up with the idea of using the new material for the channels. This was therefore where the expertise from plastics production in Andernach was combined with the concrete know-how in Rendsburg. | |||
ACO needed a special mixing and casting machine for the series production of polymer concrete channels. Only a system from RESPECTA came into question. The machine manufacturer from Wülfrath was only founded in 1969, and specialised in plants for the preparation of highly reactive mixtures. The tip about the new technology came from the Austrian sales partner Assmann. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 260 px> | |||
Datei:Dieter Brink.jpg|<br>From left, Severin Ahlmann, Kurt Tonn chairman of the works committee and Dieter Brink. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:Fertigung USA 1977.jpg|<br>The "Respecta" machine further developed by ACO, seen here after the start of production by ACO USA in 1977.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
The new machine was installed in Rendsburg on 9 March 1970. It still had a few teething problems – such as the central screw conveyor clogging up too quickly – but ACO's plant engineers found a solution. | |||
The Respecta machine was stationary. Only its movable pouring nozzle could be moved to the moulds. The initially wooden DRAIN moulds were turned upside down and filled with the viscous mass from the open underside – which was somewhat awkward. ACO's plant engineers soon constructed a new, dedicated and fully mobile machine, that moved along the production line and filled the moulds. After only 10 to 15 minutes, the strength of the channels was enough to allow the moulds to be opened. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 350 px> | |||
Datei:ACO Reith Polyfertigung 1977.jpg|<br>Casting a polymer concrete channel in Reith. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:ACO DRAIN 1973 Zone Wuppertal.jpg|<br>ACO drainage: Werth pedestrian precinct in Wuppertal in 1973, here already with | |||
the advanced DRAIN made of polymer concrete.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
The length of the first channels corresponded to the previous asbestos cement channels. They had a wall thickness of 15 mm. | |||
In autumn 1970, the production of ACO Drain NW100 could be completely converted to polymer concrete. The material used in the early days - fibre or asbestos cement – became obsolete. | |||
The improved properties of the new material - greater stability and resistance - convinced the customers. In addition, a far greater variety of articles was possible with the polymer concrete casting material. If the construction of moulds and the casting succeeded, all variations were conceivable. This laid the foundation for a wide range of drainage solutions. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== ACO and the Olympic Games - the beginning of a success story == | |||
In the spring of 1970, ACO received a spectacular major order: the Rendsburg company was to equip the new Olympic Stadium in Munich with ACO DRAIN for the 1972 Olympic Games. But it was not just about equipping the stadium, but also ancillary facilities in Munich, and stadiums at other venues. The initial volume of 1,300 metres of drainage channels was to be followed-up by an order for a further 1,000 metres. For ACO Drain's marketing and prestige, the order was phenomenal. Anecdotes and legends surround the contract negotiations with the Olympic construction committee, and the first delivery to Munich. For ACO, there was also a lot of luck involved. In the end, the superiority of the polymer concrete material was convincing. "That was sensational. Something like that doesn't happen very often in German industrial history," recalls long-serving Sales Manager Arno Ebsen. | |||
Munich was followed by other Olympic Games for ACO: Montreal 1976 would be the first appearance in North America. Over the years, ACO would equip all the Olympic Games - except the Olympic Games in Moscow. Stadiums for football world championships all over the world follow. The equipping of large arenas with drainage technology also involves completely different components that can also be made from polymer concrete: the perimeters of running tracks, and jumping-off beams for instance. This was how the company established its ACO SPORT range in the mid-1970s. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 300 px> | |||
Datei:Olympiagelaende Muenchen Luftbild.jpeg|<br>Aerial view of the Olympic Games site in Munich. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:ACO Polyester Muenchen Messe Frankreich.jpg|<br>Advertising with the Olympic Games: ACO advertises its first Olympic Games contract at a French trade fair in the 1970s. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Ernst Vollstedt - the father of the global success of ACO Drain == | |||
[[Datei:1.1.B 00054 Ernst Vollstedt.jpg|220px|thumb|right|Ernst Vollstedt, managing director of ACO Rendsburg in the early 1970s.]] | |||
At the end of the 1960s, when the retirement of Rendsburg managing director Rudolf Kobelt became imminent, Severin Ahlmann had to establish a successor, and his choice fell on Ernst Vollstedt, who was barely 30 years old. At the beginning of the 1970s, Vollstedt, a native of Rendsburg, took over the management of the site on the Kiel Canal. | |||
Vollstedt was born in Rendsburg in 1938. After completing his schooling and military service, he started working for the Severin Ahlmann company on 1 April 1960, not in Rendsburg, however, but at the new site in Reith. Barely two years after completing his training, he took over the management of the company at a young age. He interrupted his time in Reith in 1965, for a four-month assignment in the USA. | |||
In 1967, Vollstedt moved to Andernach to set up a modern logistics operation. After completing this work, he finally returned to his home town with his family in 1968, and started at ACO Rendsburg. | |||
In June 1969, at the age of 31, Ernst Vollstedt took over responsibility for the Rendsburg site. At the beginning of the new decade, Severin Ahlmann's centre of life was still in Andernach, in the Rhineland, but he spent more and more time in Pöcking on Lake Starnberg, and in Morsum on Sylt. After a series of personal crises - the failure of his second marriage, and the decline of the Carlshütte - Severin Ahlmann travelled a lot, with long stays on the Fiji Islands, and in the USA, for example. The two managing directors - Rolf Schönrock in Andernach, and Ernst Vollstedt in Rendsburg - ran the companies. | |||
Vollstedt kept his boss informed of developments in detailed letters. Later he started to write two to three reports a year on all the company's business segments. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 460 px> | |||
Datei:Jubiläum in Damp 1973.jpg|<br>From left Kurt Tonn, chairman of the works council, Ernst Vollstedt, and Severin Ahlmann, honouring the jubilarians at ACO's anniversary celebration in Damp in 1973. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
In the first few years under the aegis of Ernst Vollstedt, ACO rapidly developed into one of the leading suppliers in the drainage solutions market. With product manager Dieter Brink, sales manager Arno Ebsen, and system designer Uwe Wunderlich, Ernst Vollstedt made ACO-Drain a global success. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== ACO Drain goes international == | |||
For ACO DRAIN, the Rendsburg company entered into a sales partnership in Switzerland at the end of 1970. Studer und Thomann AG took over sole distribution for Switzerland, and from April 1973, also for neighbouring Austria. | |||
A second sales cooperation was established in France. The contract with the Ets. R. Lefèbure group, based in Mantes-la-Jolie in the Île-de-France region near the capital, came into force on 1 April 1972. Behind the group was the Lefèbure family of entrepreneurs. Vollstedt later convinced his boss Severin Ahlmann to set up a plant in France with Lefèbure. | |||
The first launch of ACO DRAIN in a northern European market took place in neighbouring Denmark. The Danish region had long been familiar to the Ahlmann family of entrepreneurs. From 5 June 1972, Sapolite A/S became the sole distributor for ACO DRAIN. Over the next few years, other polymer concrete products were added, such as the ACO Farm range. | |||
The first steps with DRAIN were taken in England at the same time. At the beginning of 1972, a partnership was formed with the businessman Malcolm Henderson, who organised the market launch, particularly in the London area. Consideration was given to setting up their own production in England, but the plan was shelved. The search for a distribution company was unsuccessful. Malcolm Henderson therefore founded "Kaskade Drains Limited" in mid-1973, which sold ACO DRAIN channels mainly in southern England. The sales figures were promising. Kaskade was able to place ACO drainage systems well in England by the summer of 1974. Around 50 major construction projects were supplied by then, including some involving prominent clients such as British Railways, or the London Port Authority. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Drainage instead of silk printing - production in Mitlödi, Switzerland == | |||
Now that a number of European markets had been opened up through sales cooperation agreements, production of ACO DRAIN was also to be established abroad. An opportunity presented itself in Switzerland in the spring of 1972. The silk printing company Mitlödi AG, located in the small town of Mitlödi in the canton of Glarus, was looking to expand its production range. | |||
The traditional Swiss silk and textile industry was in crisis. The whole sector had to reorient itself, and also open up business segments outside the traditional business. | |||
The contact came about because Severin Ahlmann sent numerous airmail letters to potential interested parties. As always, they were written in green ink, indirectly marking his leadership position. Green was traditionally reserved for the top management level in Germany's administrations. Dr. Kurt Hauser of Seidendruckerei Mitlödi AG was interested and replied. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 400 px> | |||
Datei:Seidendruckerei Mitlödi zoom.jpg|<br>The silk printing works in Mitlödi. On the left, the factory for DRAIN production with the inscription "ACO Bauelemente". <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
The deal was sealed in June 1972. The silk printing works, in which Severin Ahlmann had a one-third share, invested heavily and made a new factory building available in Mitlödi. ACO technicians assembled the machinery by the beginning of February 1973, and then also mentored the first two weeks of operation on site. At the same time, three Swiss employees were trained at ACO in Reith. The metal cast gratings were supplied by ACO Andernach. One month earlier than originally planned, production of ACO DRAIN started on the new production line on 5 February 1973. | |||
For the time being, the sole distributor in Switzerland was Studer und Thomann AG, which no longer bought its channels from ACO in Germany but from the canton of Glarus. As early as spring, Mitlödi had to increase the production output of channels from the originally planned 420 m per day. In 1974, the first full year of production, the "silk printing works" made a net profit of 226,000 Swiss francs on sales of over 2.5 million Swiss francs. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Attempted reunification: Andernach and the Carlshütte == | |||
[[Datei:53 GlückAuf Dezember 1970.jpg|280px|thumb|right|Turning back the clock and reuniting the Ahlmann companies? Even though the plan for reunification was not publicly negotiated, the cover of "Glück Auf!" from December 1970 seemed like an indirect comment on the plan.]] | |||
At the turn of 1970/71, Severin Ahlmann approached his sister Marlene Halhuber-Ahlmann to propose that the Andernach plant be reunited with Ahlmann Carlshütte in Rendsburg. Marlene Halhuber-Ahlmann’s first husband, Rudolf-August Oetker – the owner and head of the Bielefeld-based Oetker family business, and an expert in mergers and acquisitions – was called in together with his M&A team as a mediator. However, Severin Ahlmann's economic advisor Arno Seeger advised against it in view of the economic situation at the Carlshütte: merging a healthy company with a "sick company", could cause both to go under. | |||
In the end, the reunification plans do not fail because of this reservation, but because a rejection came from the Carlshütte: the investments recently made in Andernach and the resulting credit burden, were not looked on favourably by the people in Rendsburg. Moreover, it was becoming apparent that an agreement on the purchase price was hardly possible: the perceptions on both sides were too far apart. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Expansion of the product portfolio in Andernach == | |||
In Andernach, the ACO-TRENN shower enclosure designs with aluminium profiles and new panel material were launched. At the 6th International Sanitary and Heating Fair in Frankfurt in 1971, the corner cubicle in particular attracted a lot of attention. Another novelty in the TRENN programme were special bathroom modules for hotels and for the renovation of old buildings. In the same year, the new prefabricated balcony and terrace partition ACO-PRISMA was launched. | |||
The increase in turnover in Andernach was enormous: from DM 32 million in 1970, to an incredible 51.1 million in 1973, i.e., a rise of 60 percent within only three years. | |||
Bathtubs continued to make up the bulk of the turnover, with sales increasing by almost 70 percent in the three years mentioned. Business with boilers developed even better, even though their share of total sales was considerably lower at 7.6 million. Their sales quadrupled compared to 1970. The sales of ACOWELL however were declining. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=4 heights= 250 px> | |||
Datei:ACO Andernach Anfang 1970er aus Firmenbroschüre 1974.jpg|<br>Aerial view of ACO Andernach around 1970. In the foreground was the then very futuristic-looking head office building.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:Ofenbproduktion ACO Andernach Anfang 1970er aus Firmenbroschüre 1974.jpg|<br>Stove production at ACO Andernach.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:Ofenlager ACO Andernach Anfang 1970er aus Firmenbroschüre 1974.jpg|<br>View of the stove warehouse at ACO Andernach.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:Badewannen ACO Andernach Anfang 1970er aus Firmenbroschüre 1974.jpg|<br>View of the bathtub warehouse: between 1952 and 1972, ACO Andernach sold around 2.6 million cast iron bathtubs and shower trays. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery><br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 450 px> | |||
Datei:Kunststoffplattenproduktion.jpg|<br>Flat and sandwich panels were produced on technically advanced equipment – in production widths of 1.40 m and 3 m: this was the raw material for further processing into partition walls and balcony partitions.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:1.1.A 00622 NNNNNNNN ACOTrenn,037.jpg|<br>"Where others stop, that’s where ACO starts." Advertisement for ACO shower partitions in the 1970s. | |||
</gallery> | |||
The positive development was due in no small part to the Social Democrats, previously so criticised by Severin Ahlmann: in the first years of the Brandt government, the number of completed flats in the Federal Republic rose from less than 500,000 in 1970, to more than 700,000 in 1973 - never before or since has a higher figure been reached. The housing boom had a direct impact on the order books at ACO Andernach. Bathtubs, boilers and shower enclosures were in big demand. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
[[ | |||
== Arno Seeger - Severin Ahlmann's general agent == | |||
In January 1973, due to health problems, Severin Ahlmann appointed his close confidant Arno Seeger as general agent and sole member of the Board of Directors for the plants in Andernach and Rendsburg. He himself retired to sanatoriums, first to Bad Reichenhall, then to Königstein im Taunus. | |||
Arno Seeger, born in 1914, studied economics and business consultancy, and was quite well known in business circles. He was considered a "string puller", and belonged to the exclusive circle of grey eminences of the German economy. Seeger sat on many supervisory boards, advised companies along the Rhine, and was also very well connected in political circles. He began his career at Deutsche Bank. He later served as head of finance at Krupp, but left the company in the wake of the Krupp crisis in 1967. A short time later, he joined the Quandt Group as an intermediary. Seeger was also referred to as a "businessman without a business". | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
[[ | |||
== Two anniversary celebrations: 25 years of ACO == | |||
< | In October 1973, ACO Rendsburg celebrated its 25th anniversary with a big party at the Baltic Sea resort "Damp 2000". But why in 1973? – after all, SAB was founded in December 1946, so the celebration should have been at the end of 1971. In fact, it was ACO Andernach whose anniversary was celebrated in 1973! 1 November 1973 was the 25th anniversary of the establishment of ACO in Andernach. Severin Ahlmann had decided to celebrate both anniversaries in the same year, and not separately, even though this meant a two-year delay for ACO Rendsburg. | ||
<br> | |||
</ | <br> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 450 px> | |||
Datei:ACO Damp 2000.jpeg|<br>The futuristic-looking Baltic Sea resort of Damp, located on the Schwansen peninsula on the Baltic. The resort, built in the concrete brutalism style of the 1970s, was the setting for the legendary celebration of ACO Rendsburg's 25th anniversary. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
First, the company founder invited the employees of Rendsburg and Reith, together with their spouses, to a long weekend at the Baltic resort "Damp 2000" from 25 to 28 October 1973. The gigantic holiday resort on the Schwansen peninsula on the Baltic Sea had only just been opened. For the employees from Reith, there was a tour of the factory in Rendsburg beforehand. They celebrated for three days in the hotel complex. Room and board were free for the employees. All the hotel's leisure facilities could be used. The celebrations were legendary, and people at ACO still talk about Damp today. Severin Ahlmann shone with his engaging, charismatic personality. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 280 px> | |||
Datei:Damp 1973 Gesamtbild der Bühne.jpg|<br> <br> <br> | |||
Datei:Damp 1973 Ehepaar Wolf.jpg|<br> <br> <br> | |||
Datei:Damp 1973 Gretel Beyer.jpg|<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
< | A week later, there was also a day and a half of celebrations in Andernach. A small tent city with a restaurant, dance hall and a circus were set up in the company grounds. The renowned caterer Käfer from Munich-Bogenhausen, took care of the catering. Severin Ahlmann gave one of his famous humorous speeches. From the family circle, his now 21-year-old nephew Hans-Julius Ahlmann, and Severin's niece Katharina Halhuber-Ahlmann, the eldest daughter of his sister Marlene, also took part. | ||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
</ | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=3 heights= 280 px> | ||
Datei:25 jahre Andernach 1973 Festzelt.jpg|<br>The marquee on the company premises waits for the guests. <br> <br> | |||
Datei:1.1.B00024 1973NNNN Jubiläum 117 bearbeitet.jpg|<br>Inside the marquee, everything was prepared for the arrival of the guests.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:25 Jahre Andernach HJA.jpg|<br>On the right, Hans-Julius Ahlmann, in the middle, Katharina Halhuber-Ahlmann, on the left, Dr Emmerich Assmann. <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
When part of the tent city burnt down in the night after the end of the celebrations - the cause of the fire could not be clarified - it seemed like a bad omen for what would happen in Rendsburg a few days later. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The explosion incident in Rendsburg == | |||
[[Datei:1.1.B 00097 Kirschkowski in der Mitte.jpg|250px|thumb|right|Reinhard Kirschkowski (centre), one of the victims of the accident, here in a photograph from the early days of SAB.]] | |||
On 9 November 1973 at 12:38 p.m., a "violent bang" startled Büdelsdorf. Immediately, "a huge jet of flame" could be seen over the ACO site. | |||
An explosion in the ACO DRAIN production factory! Chemicals for the production of the polymer concrete mixture exploded. Part of the building was immediately destroyed, and the resulting fire led to further destruction. 14 employees were in the building at the time of the explosion. The accident occurred shortly after the shift change at the stationary plant. ACO employee Uwe Wunderlich immediately alerted the Büdelsdorf fire station, which really quickly started extinguishing the fire. | |||
Severin Ahlmann's sister, the doctor Dr. Marlene Halhuber-Ahlmann, was not far from the scene of the accident in her parents' house on the neighbouring Carlshütte site, and rushed to the scene of the accident where she administered first aid. Severin Ahlmann was in Andernach at the time of the explosion. | |||
Nine people suffered severe burns, and another three minor burns and injuries. Reinhard Kirschkowski died directly at the scene of the accident. In addition to the fire brigade and rescue workers, the criminal investigation department was soon on the scene, questioning the employees who had been present. | |||
< | A few hours after the explosion, workers Albert Bahrt, Herbert Jasker and Günter Noch, died from their injuries, in the Rendsburg city hospital. One week later, Dieter Schmidt also died in the Berufsgenossenschaftliche Unfallklinik in Ludwigshafen-Oggersheim. A total of five people lost their lives. | ||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 300 px> | |||
Datei:Werkshalle1 Explosionsunglück 1973.jpg|<br>View of factory building 1 damaged by the explosion.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:Polymischanlage Explosionsunglück.jpg|<br>The polymer concrete mixing plant, badly damaged by the explosion.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[Special:MyLanguage/#top|↑ nach oben]] | [[Special:MyLanguage/#top|↑ nach oben]] | ||
== Aftermath of the accident == | |||
The accident had a direct impact on the company's approach to hazards and safety. Until that autumn in 1973, there had been no major accidents at ACO - despite the predominantly strenuous physical work, as well as the multiple use of heavy equipment. The relatively new source of danger, chemicals for resin production in polymer manufacturing, had been well under control up to then - for more than three and a half years. | |||
The first consequence of the explosion in Rendsburg was the shutdown of polymer concrete production in Rendsburg, then also in Reith. The safety measures were reviewed and modified. Standards were raised to the highest level in cooperation with the Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing. | |||
On 21 January 1974, DRAIN production in Reith was restarted. And in Rendsburg a new concept of polymer concrete production with increased capacity was implemented at the beginning of April 1974. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Acrylic bathtubs - the missed opportunity for ACO Andernach == | |||
After rival companies such as Hoesch and Kaldewei launched acrylic bathtubs - as an alternative to the traditional cast iron bathtub - ACO presented the first round bathtub made of fibreglass polyester, with only an acrylic gelcoat, at the 1973 Frankfurt sanitary trade fair. Managing director Rolf Schönrock, however, did not consider such a niche product to be sufficient. He wanted to get into acrylic bathtub production. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 350 px> | <gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 350 px> | ||
Datei: | Datei:Hoesch Sanicryl-erste Acryl-Badewanne in Deutschland.jpg|<br>In 1972, the Hoesch Group launched Germany's first acrylic bathtub with the name Sanicryl. (Source: Hoesch Design GmbH) (Quelle: Hoesch Design GmbH)<br> <br> | ||
Datei:1.1. | Datei:1.1.A 00167 1974NNNN ACOBroschüre,007a.jpg|<br>ACO's round bathtub made of fibreglass polyester with an acrylic gelcoat goes into series production. <br> <br> | ||
Datei: | </gallery> | ||
Datei: | |||
On Schönrock's initiative, negotiations about a cooperation were held with the Scottish bathtub manufacturer Carron. Carron was initially to produce acrylic bathtubs for ACO for sale on the German market in two standard sizes. Then the Scots were to help set up ACO’s own acrylic bathtub production in Andernach. But this would require considerable investment. Severin Ahlmann hesitated. When the negotiations with Carron reached the crucial phase at the beginning of 1974, the company owner was on business overseas General manager Arno Seeger hesitated to make such a far-reaching strategic decision without consulting the company owner. No deal was reached. | |||
In his autobiography, Severin Ahlmann retrospectively described it as a "serious entrepreneurial mistake" not to have started production of acrylic bathtubs. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== The Carlshütte in the 1970s == | |||
DThe Carlshütte underwent a cautious modernisation process in the late 1960s and early 1970s after a long standstill. Its main product was still bathtubs, but other traditional branches of production, overtaken by market developments, were gradually abandoned. This included, for example, the production of stoves, which ended in 1972.<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 700 px> | |||
Datei:Luftaufnahme CH aus Geschichte CH 1977.jpg|<br>Aerial view of Büdelsdorf around 1970. In the foreground the ACO site, in the centre the Carlshütte, whose products were now marketed under the name of Ahlmann. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
At the same time, new segments were opened up. Continuous casting, i.e., the production of prefabricated raw material and semi-finished products from iron alloys, proved to have a promising future. However, it required significant investments in new plants. | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 350 px> | |||
Datei:Strangguss in CH aus Geschichte CH 1977.jpg|<br>The new continuous casting plant at the Carlshütte. Today, ACO Guss in Kaiserslautern is the market leader in continuous casting with this and new plants. <br> <br> </gallery> | |||
In 1970, the foundry built a continuously operating cupola furnace with a capacity of 9 to 15 tonnes per hour for DM 8 million. Four electric induction furnaces were installed downstream. The new facilities, with contemporary dust removal technology, were also good for the environment - the air quality in Büdelsdorf and the surrounding area improved considerably. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
Although the name Carlshütte was still very much present, the company now traded simply as Ahlmann GmbH. The production of swing loaders, which started in the early 1950s, had been outsourced to the independent company Ahlmann Maschinenbau GmbH since 1972. Here the company was doing successful business with the completely newly developed AS 7 and AS 12 models, which went into series production in 1969 and 1972 respectively. | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 350 px> | |||
Datei:Produktion AS7 aus Geschichte CH 1977.jpg|<br>1969 saw the series production at Ahlmann of the newly developed AS 7 swing loader. It had a 69 HP engine, and the bucket had a capacity of 1 cubic metre. <br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
Ahlmann GmbH wanted to open up a new promising business segment with the production of prefabricated baths. After one year of development, the Ahlmann complete bath was presented at the 1973 International Sanitary and Heating Fair in Frankfurt, under the name "Badinet". A little later, shipyards also approached Ahlmann with the request for prefabricated bathroom solutions. The Badinet was further developed into the Marinet, a prefabricated bathroom module for shipbuilding. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=2 heights= 320 px> | |||
Datei:Marinett aus Geschichte CH 1977.jpg|<br>The Marinet - the prefabricated module was transported to the assembly site by forklift truck and crane.<br> <br> | |||
Datei:CH Messe ish 1973.png|<br>Ahlmann's stand at the 1973 International Sanitary and Heating Fair in Frankfurt. Glück auf!" noted: "The Ahlmann stand was again a special attraction. At the old location, but with a new face and real surprises. The "Badinet" alone, fully equipped and "with live models", caused a stir, not only among the sanitary specialists: a catwalk that allowed educational insights from a bird's eye view had to be temporarily closed..<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Crisis at the Carlshütte == | |||
In the midst of the restructuring process that the Carlshütte was undergoing, the Federal Republic was rocked by the biggest economic crisis in its experience. In the spring of 1973, the Bretton Woods world monetary system collapsed. Until then, this had stimulated world trade by largely stabilising exchange rates, and made it largely independent of exchange rate risks. Now the value of the German mark rose considerably against the currencies of the most important trading partners, for example, by more than double against the US dollar. | |||
For an export-oriented company like the Carlshütte, which marketed its products worldwide, this was a disaster. Carola bathtubs, for example, became more expensive abroad. At a stroke, they were no longer competitive on the world market. | |||
Then there were the new products from competitors. These were the classy plastic bathtubs mentioned above, and the enamelled steel bathtubs produced in large quantities, especially by Kaldewei. These were lighter than cast iron bathtubs , and were therefore easier for plumbers to handle. | |||
The first oil crisis also followed in 1973. It was triggered by the Organisation of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), whose members decided in October to cut their production in response to the Yom Kippur War, in order to exert political pressure on the West. Within a few months, the price of crude oil quadrupled, and the prices of other commodities also continued to rise. Economic activity dived to an extent unprecedented in the history of the Federal Republic in 1974, especially in the construction industry, which was so central to Ahlmann. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
== Bankruptcy of the Carlshütte in 1974! == | |||
In September 1974, the companies Ahlmann GmbH and Ahlmann Maschinenbau GmbH, which had emerged from the long-established Carlshütte, had to file for bankruptcy after almost 150 years of successful operation. The Ahlmann family left the Carlshütte. The Hamburg ship salvage entrepreneur Ulrich Harms bought the Carlshütte at a "junk price", as the news magazine DER SPIEGEL put it. He paid DM 13.7 million. | |||
After considerable investment and restructuring, the Carlshütte could continue to operate with a significantly reduced number of employees, and a changed product range. The focus was still on foundry, mechanical engineering and sanitary ware. | |||
In 1998, Harms also went bankrupt and died. The Carlshütte was dissolved and sold at auction. It was Hans-Julius Ahlmann who bought back the site and buildings, so that ACO and the Carlshütte were finally reunited geographically and idealistically. Since then, the historic aisles and the grounds of the Carlshütte have been filled with new life, now as a venue for NordArt, one of the largest exhibitions of contemporary art in Europe also known as Kunstwerk Carlshütte. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 800 px> | |||
Datei:Kur-am-Kai.jpg|<br>A report in the news magazine DER SPIEGEL on 17 February 1975 took a critical look at the business practices of the new Carlshütte owner Ulrich Harms.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
== The sale of ACO Andernach == | |||
[[Datei:1.1.A 00849 Arno Seeger2.jpg|300px|thumb|right|]] | |||
The bankruptcy of his parents' company, the Carlshütte, plunged Severin Ahlmann into a serious personal crisis. He felt guilty. In addition, he divorced his second wife Maria in the same year. | |||
The economic crisis also affected ACO Andernach. In the course of 1974, there was a massive slump in sales. The optimistic growth targets were suddenly a long way off. Only three weeks after the bankruptcy of the Carlshütte - at the beginning of September - Arno Seeger offered to take over the Andernach plant at a very favourable price, namely only DM 1 million. On 23 September 1974, the contract was signed. Seeger had the right to use the old company name and the ACO brand name until 1982. | |||
Thus, in 1974, the entrepreneurial activity of the Ahlmann family also ended in this company. | |||
[[#top|↑ to the top]] | |||
= Review and outlook: ACO on the road to success = | |||
From 1974 onwards, Severin Ahlmann's entrepreneurial activities were concentrated entirely on ACO in Rendsburg, which was founded in 1946, and its branch factory in Reith in Lower Franconia. A magical rise began for the small company ACO. In eight years, sales rose from DM 12 million to DM 43 million, largely driven by ACO Drain. | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 400 px> | |||
Datei:ACO Drain Bilanz 1978.jpg|<br>The 1970s saw a steep rise in turnover - the success was mainly due to ACO Drain.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
This success bears a number of names: at the top, the young, highly dynamic managing director Ernst Vollstedt, a true ACO homegrown, the great sales director Karl-Arno Ebsen, the father of the ACO Drain channel system Dieter Brink, and Uwe Wunderlich, the builder of the first polyester concrete plant. All four of them are still around, and in their retirement, can look back with immense pride on achieving this unique success in their lifetimes. | |||
At the end of 1978, however, the run was over for a while. It did not go much higher for the time being. With the establishment of ACO companies in Switzerland, France and the USA, and numerous foreign agencies, the company had perhaps overstretched itself somewhat, and needed a breather. | |||
When Hans-Julius Ahlmann politely asked his uncle in the course of 1980 whether he could use him - he was employed by MAN in Augsburg at the time - he immediately agreed. On 2 May 1981, Hans-Julius Ahlmann started work in Rendsburg. | |||
< | In the 40 years since then, ACO has grown into a large company, positioned worldwide, with a very strong brand and a turnover of 1 billion. This has been made possible by our employees, a lot of luck, and our corporate culture, which tries to bring out the entrepreneurial spirit in as many of us as possible. And some of us have been able to realise their own entrepreneurial visions of a lifetime. So may it continue... And the first billion, they say, is supposed to be the hardest… | ||
<br> | |||
</ | <br> | ||
<gallery mode="packed" perrow=1 heights= 400 px> | |||
Datei:Umsatzgrafik Video gestaucht.jpg|<br>In the 40 years, sales grew 40-fold to 1 billion.<br> <br> | |||
</gallery> | |||
Today, the ACO Group is represented with sites and production facilities in more than 40 countries. See also [https://www.aco.com/en/contact/aco-group-worldwide ACO group worldwide.] | |||
<br> | |||
< | <br> | ||
The ACO Wiki does not end here, it remains exciting right up to the present day. It will be expanded step by step in the coming months with more history and stories from and about ACO. | |||
Enjoy reading, browsing and discovering! | |||
Your ACO Wiki Team | |||
= Imprint and Picture Credits = | |||
---- | Here you find the [[Aco_Wiki:Impressum_und_Bildnachweis|imprint and picture credits.]] | ||
-------- | |||
Aktuelle Version vom 10. Dezember 2021, 10:20 Uhr
The ACO 75th Anniversary History Wiki
Welcome to the ACO History Wiki, which is launched in ACO's anniversary year!
The Wiki contains exciting stories about ACO. The history of the company's founding and its early years, locations and subsidiaries, products and services, employees, customers and suppliers, working life and the Ahlmann family of entrepreneurs – these are all topics that are presented in pictures covering the many years of the company’s history. Interesting correlations become clear, insights possible, and also amusing facts come to light. Here you can find out everything about how the globally-active world-market leader in drainage technology, gradually developed from small regional beginnings in Büdelsdorf in Schleswig-Holstein.
The Wiki is an ongoing project that is constantly being expanded. By the 75th anniversary of the company's founding in December 2021, the first decades of the company's history is researched and documented. In the coming months, more stories and tales from and about Aco will be presented here.
You are welcome to contribute to this project. Do you have pictures or documents on any aspect of ACO’s history? Can you think of any stories that are "typically ACO"? We look forward to your contributions. Contact us at: info@history.aco ! (as of December 2021)
The history of ACO
ACO - Foundation and first years 1946 to 1949
ACO's origin: the Carlshütte
ACO is a spin-off from the venerable Carlshütte foundry, which is steeped in tradition, and was established in 1827 – almost 200 years ago – in Büdelsdorf near Rendsburg in Schleswig-Holstein. The Carlshütte was the very first industrial enterprise on the Jutland peninsula and, above all, the first ironworks in the whole of Denmark. The founder was the merchant Markus Hartwig Holler. He ran a flourishing timber business in Rendsburg, but wanted to build an iron foundry in Büdelsdorf.
Holler was completely in tune with the times. He recognized the importance of iron as a material for the new industrial era. In a petition to the Danish King Frederick VI, he meaningfully states:
"It is the word “iron” that explains everything".
He goes on to write that iron is "equally useful, indeed indispensable, for the state and national defence, as it is for households, farmers, trades, buildings and factories. After a visit by the Danish King Frederick VI in June 1829, the King was so impressed by Holler's work, that on his return trip he issued instructions to make Holler a Knight of the Order of Dannebrog. In the picture on the right, Holler's chest shows the medal of the Order of Dannebrog, which is still awarded today as an order of merit for civil and military service to loyal servants of the Danish state, and for special merits in the arts, sciences or economic life.
The Danish king's governor of the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, Carl von Hessen, supported the venture from the beginning. In gratitude, Holler named the ironworks "Carlshütte" after him. The Landgrave, who was already over 80 years old at the time of the company's foundation, was descended on his mother's side from the English royal house of Hannover, and was the father-in-law of the Danish King Frederick VI. Carl von Hessen was the great-great-great-grandfather of the recently deceased Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, Prince Consort of the British Queen Elizabeth II, who in 2006 presented ACO with "The Queen's Award for Enterprise".
Thus, the circle closes.
Carl was influenced by the ideas of the Enlightenment. He was interested in culture and science. He studied metallurgy and metal casting. He had a particular soft spot for alchemy. Thus, until the end of his life, he endeavoured to extract gold from an alloy of base metals. This passion could also have been a motive for his support of the Carlshütte. Irrespective of this, however, Carl von Hessen was regarded as an avid promoter of business and new industrial ventures.
The second patron and protector of the Carlshütte was the Danish King, Frederick VI. Like his governor, Carl von Hessen, he was fond of science and business. He was quickly convinced by Markus Hartwig Holler's ideas. At an audience in Rendsburg, Holler was able to present the plans for establishing the foundry in person. The king even visited the foundry construction site.
Over the next ten years, Frederick VI visited the Carlshütte again and again. As in 1829 for example, when Holler was able to report on the first tapping of the smelting furnace. In 1831, Frederick VI visited the blast furnace construction site, and he was back in Rendsburg again in 1835. The king's fifth and last visit took place in 1839: the Carlshütte was in full swing, and Holler was able to present the king with a steam engine that was built there. The founder did not forget that the economic upswing was due in no small part to a number of privileges granted by the monarch. These included the duty-free import of raw materials, the duty-free export of iron goods, and protective tariffs against foreign products.
However, the blast furnace only worked for a few years. The production of iron from bog iron ore, which occurs in Schleswig-Holstein in readily usable quantities, proved unprofitable, so smelting was abandoned, and the company switched exclusively to foundry operations.
The Carlshütte produced cast-iron utensils and objects for the household, road construction, agriculture and shipbuilding. Fascinatingly, the Carlshütte had products in its range that ACO also manufactures today, albeit with different materials. These are window frames, cribs and troughs, and animal pens, also sewer and manhole covers, light oil separators, gutters with cover grates, and finally, sanitary items such as bathtubs and cast-iron water closets.
The Ahlmann family at the Carlshütte
The Ahlmann family was to play a key role in the development of the Carlshütte, and in the founding of ACO. The German-Danish merchant and entrepreneurial family Ahlmann has been resident in Denmark and in the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein since the 16th century. Thomas Jörgen Ahlmann, the great-great-grandfather of Hans-Julius Ahlmann, established the first connection with the Carlshütte in 1840. He went into business with Holler, and set up a commission warehouse for the Carlshütte's goods in Fredericia, Denmark. From here, Carlshütte products were distributed to the Scandinavian countries. At the time, there were no agents, but instead, wholesalers who were trusted partners.
Thomas Jörgen Ahlmann also founded the distillery & brewery "Ahlmann & Co" in 1842. This company name, especially the abbreviation "ACO" , will become of particular importance more than a hundred years later.
Thomas' second eldest son, Johannes Ahlmann took over his father's business together with his brother-in-law Dethlef Ohlsen, which then traded as "Ohlsen & Ahlmann" from 1878. In the following year, the two merchants moved the Carlshütte commission warehouse to Copenhagen. Hartwig Peter Holler – the son of the founder of the Carlshütte – was so convinced of Johannes Ahlmann's abilities that he offered him the post of commercial director at the Carlshütte, which he accepted in 1883. At this time, the Carlshütte was a public limited company. Over the next few decades, Johannes Ahlmann modernised the company, expanded it, and introduced new products, especially enamelled bathtubs, which made the Carlshütte world-famous. In 1900, more than 1,000 workers were employed in the company. The Copenhagen enterprise was later sold to the large Danish trading company Brødrene Dahl.
In 1907, Johannes Ahlmann's son Julius joined the Carlshütte. Julius succeeded his father as commercial director in 1919, and continued the successful modernisation course. However, he died of a serious illness in 1931. His widow Käte Ahlmann was determined to preserve the company's heritage for the next generation.
In 1937, she succeeded in acquiring all the shares for the family, and transformed the public limited company into a KG. Käte Ahlmann took over the management of the Carlshütte, which from then on was a family business. In the same year, parts made of asbestos cement were produced for the first time. This gave rise to a concrete division.
The beginnings of the concrete division – use of substitutes for iron
Substitute for cast iron feet for bathtubs at the Carlshütte
The forced conversion of the German economy to war production from the mid-1930s onwards gave rise to manufacturing restrictions in the steel and iron industry: metals were to be saved in the civilian sector so that they could be used for armaments. Central to this was the 1936 Four-Year Plan, with which the economic and military war capability of the German Reich was to be achieved within four years. Within the framework of the Four-Year Plan, the bathtub industry undertook to produce models with a minimum of iron components. From April 1937, the factories were ordered to no longer use cast iron feet for built-in bathtubs. The Carlshütte found a replacement in just a few months: bathtub feet and pedestals were initially made of stoneware, and later in the year they were also made of concrete.
Further savings of iron
On 15 August 1937, the iron and steel supervisory authority ordered a production restriction of 30 percent compared to the production from 1 July 1935 to 30 June 1936 in the entire sanitary and sewer castings sector. This dramatically affected the Carlshütte. Initially, it was possible to fall back on stocks. Thus, from August to December 1937, the Carlshütte recorded only a 17.5 percent decline in sales of foundry products. Asbestos cement panels were used as a substitute for cast-iron underlays for continuous firing furnaces, and these were then also used for the back walls and floors of coal and gas cookers. Iron savings of 20 kg per cooker were achieved with the asbestos cement panels. The Carlshütte annual report of 1937 described the consequences of the manufacturing restrictions and bans: "The sales policy during 1937 was therefore essentially determined by the question of raw material procurement and the use or creation of adequate substitutes."
Cast terrazzo for the wash fountains, fireclay and ceramics for stoves
In 1938, Carlshütte pushed ahead with the use of substitute raw materials. Terrazzo – a mixture of colour-selected aggregates, water, lime and cement – was used as cast terrazzo for the Carlshütte washing fountains, which were previously made of cast iron. For the ovens, fireclay walls were installed in place of the cast-iron walls to save iron. Further savings were achieved by using ceramic ash boxes. New to the Carlshütte range were concrete boiler stoves, which were delivered from March 1938. With the compulsory use of the new materials, which were not characteristic of an iron foundry, a concrete division was set up at the Carlshütte, from which the Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB), later ACO Severin Ahlmann, was established.
Josef-Severin Ahlmann – responsible for the concrete division at the Carlshütte.
The Second World War broke out in 1939. Käte Ahlmann's sons Hans-Julius and Josef-Severin were called up for military service. The factory survived the war largely unscathed. In May 1945, Käte Ahlmann's second-born son Josef-Severin returned from the war. Schleswig-Holstein, including Büdelsdorf, was part of the British occupation zone.
The Carlshütte family business was subject to production restrictions imposed by the military government. However, it was allowed to produce concrete parts for civilian purposes. These were "simple building slabs", agricultural troughs and cement roof tiles.
Josef-Severin immediately took over management tasks in the company on behalf of his mother. He took care of the concrete production at the Carlshütte. At the age of 22, he became department head of the Carlshütte concrete division.
Severin's brother Hans-Julius also returned from captivity at the beginning of 1946. He had already had power of attorney for several years, and was designated by his mother as her successor in the management of the Carlshütte.
Establishment of Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB), later ACO
In the course of 1946, Käte Ahlmann, and Hans-Julius and Severin Ahlmann, decide to spin off the concrete division from the Carlshütte as an independent company. The background to this was fear that the Carlshütte would be dismantled by the Allies. On 1 October 1946, the British military government informed the Carlshütte management that the plant was earmarked for dismantling as part of the reparation demands.
The specific reason for the timing of the company establishment before the end of the year was the result of the local elections in Schleswig-Holstein on 13 October 1946, in which the SPD won 41.1 percent of the vote. It was assumed that the Social Democrats would also gain a majority in the state elections scheduled for the following year. The worry was that they would implement expropriation plans. The Social Democrats and the trade unions propagated the expropriation of key industries or companies that were involved in the armaments industry during the Second World War, including the Carlshütte. Käte Ahlmann wrote in a letter on 13 December: "We thought this measure (meaning the company registration) was still the right thing to do in the old year, since one never knows what new prohibitions will come at the end of this year."
In order to secure at least one segment of the business for the family, Josef-Severin Ahlmann registered the company "Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie" with the Kiel Chamber of Industry and Commerce on 10 December 1946. SAB, as the company name was abbreviated, later became ACO.
The product range of Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB, later ACO)
It was clear from the company registration letter that the production of new articles was to be started step by step. Three product groups were mentioned: Firstly, building materials for house construction: such as hollow blocks, slabs and lightweight panels, beams and rafters, as well as stair treads. Furthermore, products for civil engineering were also to be manufactured. These included posts, pavement slabs, kerbstones, pipes and cable fittings, driven piles, as well as manhole covers, street drains, cesspits and septic tanks. Finally, it was planned to also produce "non-building materials", meaning products for interior finishing, such as concrete boiler stove jackets and, in particular, terrazzo goods, such as sinks and washbasins.
The articles of the first and second product group were the main priority, explained Severin Ahlmann, because they were "particularly important for the reconstruction of the destroyed cities". In Kiel, for example, 35 percent of all buildings were destroyed, 40 percent were damaged. In the future expansion of labour, more women were to be employed. Production was to be set up accordingly.
The letter concludes with a reference to good order prospects because the Carlshütte intended to successively transfer the entire concrete production to the new Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie.
The company registration at the Kiel Chamber of Industry and Commerce was processed quickly. The trade registration certificate with the number 891/46 for the trade "concrete industry" – the birth certificate of ACO, so to speak – was issued on 19 December 1946. The retroactive effect to the 10th of the month was noted.
Company headquarters in Rendsburg - production facilities in Büdelsdorf
The company's first registered office was not in Büdelsdorf, but Rendsburg. The address was Holsteiner Straße 24, where the Carlshütte kindergarten was also located. Severin Ahlmann later liked to say:"ACO was founded in a kindergarten on an Eider lock." The address – some distance from the Carlshütte – underlines the character of an independent establishment. It was a strategic decision vis-à-vis the authorities.
The production facilities, however, were located on Hüttenweg in Büdelsdorf on the Carlshütte site. Käte Ahlmann leased the site and buildings to SAB.
The first company headquarters at Holsteiner Straße 24 in Rendsburg. Gesa Meyer, the daughter of the first managing director Paul Meyer, was one of the kindergarten children at the time and recalls: "Our father's office was on the ground floor, to the left of the main entrance, and just behind it was Josef-Severin Ahlmann's office, with a wonderful soft, dove-blue carpet."
Workforce and products
Carlshütte and SAB were closely connected. Friedrich Sensen, Käte Ahlmann's deputy at the Carlshütte, recommended his brother-in-law Paul Meyer as an authorised signatory and de facto managing director of SAB. Meyer had a decisive influence on the company in the early years at Severin Ahlmann's side. He was instrumental in SAB's success.
At the time of the company's registration, SAB had only eleven employees. Soon the number of employees rose to 100. From the beginning, Severin Ahlmann employed refugees and displaced persons from the former German eastern territories, and the Soviet occupation zone. They became a success factor for the young company.
The warehouse (factory building IV) at SAB. Concrete roof tiles can be seen on the right. For the British Rhine-Army and other British services, Carlshütte produced 42,000 stoves in 1945/46, 40,000 Canada stoves, 40,000 cookers, 100 large cookers, 3,500 bath tubs, 10,000 radiators, 5,000 washing kettles and also 50,000 aluminium roof tiles. Concrete was also used for roof tiles. This production was done on a large scale by SAB. Concrete roof tiles are an important product for SAB. Gerd Ostryga, who started at the Carlshütte on 17 November 1946, and shortly afterwards moved to the new Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB, later ACO), recounts in his memoirs that one of his first tasks was to form concrete roof tiles.
The first logo of SAB (later ACO)
The first logo of the newly founded Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie consisted of a coat of arms with stylised Ahlmann lettering. The coat of arms originally came from Bankhaus Ahlmann in Kiel, and was used by Severin Ahlmann to highlight the long family tradition. The logo was later used as a model for the logos of other Ahlmann companies.
Work under difficult conditions
The production permit for SAB did not arrive until March 1947. Until then, the permit issued to the Carlshütte was valid.
Production was by no means easy in the post-war period. There were shortages everywhere. This applied to food and everyday items, as well as to raw materials and energy. Parts of the infrastructure were still not repaired. Almost all resources were regulated by the authorities.
At the end of March 1947, the city of Rendsburg allocated SAB a certain amount of electricity: 15,000 kWh per month.
In mid-May 1947, the Rendsburg post office informed Severin Ahlmann that his application for "Permission for unrestricted voice telephony within the British zone" was granted. He had to wait a long time for this: the application had been submitted six months earlier. Severin Ahlmann was able to keep an existing telephone number - 2555. In addition, he was given the opportunity to register for call prioritisation by dialling a specific code number.
The foundation of Ahlmann & Co. in Andernach
On 1 November 1948, Ahlmann & Co. was founded in Andernach, Rhineland-Palatinate. The aim of establishing this company – similar to the establishment of Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie two years earlier – was to secure the family and its entrepreneurial activities in view of the uncertain political and economic future. Andernach was located in the French occupation zone. It was hoped that dismantling and expropriation plans would be pursued less intensely here, or not at all. Moreover, Käte Ahlmann, who comes from the Rhineland, had close ties to the region.
Another reason for the Ahlmann family to hedge their bets was the beginning of the "Cold War". The blockade of Berlin by the Soviet Union fuelled the fear of escalation. Andernach, which was further away from the East Zone border, and lay mainly on the other side of the Rhine, appeared to be a "safe fallback location" in case the Red Army advanced to the Rhine.
Purely economic motives also played a role. An iron foundry and an enamelling plant were to be built in Andernach. The product range corresponded to that of the Carlshütte: cast iron tubs, washers and other sanitary castings. The new plant was an extension of the Carlshütte, which was to supply the French and American zones with these products.
The project was approved at the beginning of February. At the end of May 1949, construction work began and progressed rapidly. In the following years, there was an exchange of personnel between Severin Ahlmann-Betonindustrie (SAB) and the newly founded company in the Rhineland. This was accompanied by a fruitful transfer of know-how.
Another important aspect: Ahlmann & Co. later provided the abbreviation for the group's current name: ACO. Josef-Severin Ahlmann later recalled that the business liked to refer to Thomas Jörgen Ahlmann's company Ahlmann & Co. established in Fredericia in 1842.
SAB in 1949
Käte Ahlmann was exonerated in the denazification proceedings, the accounts were unblocked, the Carlshütte was not dismantled.
However, a reincorporation of concrete production into the Carlshütte was not an issue. SAB remained an independent company, had made a name for itself, and was growing. In 1949, the turnover was DM 665,000, more than four times the turnover two years earlier. The number of customers doubled in the same period. In 1949 there were 550.
Severin Ahlmann had married in the meantime. His wife Maria Luise, née Guthe, worked in the company. A photo album made by Severin Ahlmann in 1949 gives an insight into the early days of the company.
You can browse through the entire photo album here.
Severin's dedication to his mother Käte Ahlmann. He wrote: "To our mother! 'We don't celebrate anniversaries - we celebrate successes!' We also want to claim this saying for ourselves, and can state with satisfaction that the foundations for the future have been laid. With heartfelt gratitude for entrusting us with this ongoing task. Your Josef-Severin. 24.12.1949"
Severin Ahlmann's involvement in the Carlshütte and SAB (ACO) 1949 to 1956
The business development of SAB (ACO) in the early 1950s
The young SAB developed extremely positively in the early years. At the end of the fourth business year in 1950, the turnover of DM 1,600,000, was ten times that of the first full year in 1947. The customer base had almost quintupled in this short time, to 965. Most of the customers still came from northern Germany, from Schleswig-Holstein and the Hamburg area. However, Severin Ahlmann announced as early as 1951 that the company had "increasingly succeeded in opening up the German markets south of the Elbe."
By 1951, the workforce had grown from the initial eleven employees to around 100, confirming the positive trend.
Whereas at the very beginning, large orders from customers could often not be processed due to the limited production capacities, this situation improved at the beginning of the 1950s. There was major investment: new, modern machines made higher order volumes possible. And if production also had more space to develop, then even more could be made.
In the spring of 1951, the company founder emphasised the "importance of our company in the Rendsburg economic region". The local and state authorities saw it similarly, and supported the young company; this was also because Severin Ahlmann had tailored his production to urgent, very current problems: SAB manufactured the articles needed for reconstruction.
Securing raw materials - the acquisition of the Mielberg gravel plant
In 1950, SAB secured the future supply of aggregate. This is the term used to describe mineral additives - from sand to gravel – that, when combined with water and cement as a binding agent, produce concrete.
In February 1950, Severin Ahlmann acquired the gravel plant in Mielberg, municipality of Jagel, in Schleswig, from Struve & Weyhe. The purchase included a workshop, a silo, various machines, such as scraper and screening plants, conveyor belts, pumps and electric motors, as well as a range of small equipment. And it also included the production rights. In 1943, Struve & Weyhe had concluded an extraction contract for a plot of land of about three hectares belonging to the Mielberg farmer Johann Gerold. This allowed the company to extract stones, gravel and sand from the ground there.
SAB took over all existing delivery obligations, as well as the employment contracts of those who had been working in the gravel pit before the takeover.
Entrepreneurial activities of the Ahlmanns in the young Federal Republic of Germany
For Severin Ahlmann in the 1950s, however, SAB is "only" one building block in a company complex centred on the Carlshütte.
After the plans to dismantle and expropriate the Carlshütte had been averted, Käte Ahlmann devoted herself to a wealth of new activities. In doing so, the now almost sixty-year-old businesswoman unleashed an enormous amount of energy. Her sons Severin and Hans-Julius were also involved with passion and vision.
To help alleviate the still acute housing shortage, the family founded the "Gemeinnützige Wohnungsgesellschaft A GmbH" in early 1949. In addition to the Carlshütte, Severin's SAB also financed the new company, which primarily created cheap housing for the many displaced persons. In September 1949, the topping-out ceremony for the first construction phase of a housing estate with 36 flats was celebrated.
With the upswing of the Carlshütte, and the good economic development of SAB, the transport volume also increased. As a consequence, Ahlmann-Transport KG was founded in September 1950. The company was entered in the commercial register on 25 October 1950, with Severin Ahlmann as the owner, and his brother Hans-Julius as the authorised signatory. Branches were opened in Hamburg and Bremen. The new company transported goods by truck and rail. It also loaded ships. And what's more: Ahlmann-Transport KG also acted as a shipping company, running scheduled services, and commissioning the construction of ships, which are used in a variety of ways. Friedrich Sensen, Kätes' confidant and the grey eminence of the Carlshütte, played a decisive role as managing director of Ahlmann Transport KG.
There are three main reasons for the investment in ships: the Carlshütte is located far away from its sources of raw materials, and partly also from the areas where its products were sold. A major advantage, however, is its location on the Upper Eider, with access to the Kiel Canal. It also had a history of shipbuilding. A factory-owned shipyard was built on the Eider in 1847, and it had traditionally maintained a number of ships bearing the name "Carlshütte" with consecutive numbers. After the Second World War, the German merchant fleet was destroyed, and was to be rapidly rebuilt by German companies. The creation of new shipping capacities was therefore fiscally subsidised.
The overseas connections
Further steps in the transport business follow: in April 1951, Translanta GmbH was founded as an independent shipping company. The company was based in Rendsburg.
New ships were also built especially for Translanta: the ocean-going vessels COLONIA and CIANDRA, commissioned in 1952 and 1953.
The ships were equipped with "particularly nicely furnished passenger cabins". The salons designed by Severin with mirrored floors and cowhide rugs, which came from cows on the Ahlmann farm on the Carlshütte that grazed where the "Rondo" is today, caused a sensation. Of course, the bathtubs from the foundry are not missing either – at that time an almost unheard-of luxury on ships of this class.
The COLONIA and CIANDRA sailed on the Ahlmann Trans Caribbean Line from the Great Lakes in Canada to the Caribbean: the first route for German ships between foreign ports in the post-war era.
Severin Ahlmann traveled a lot on business during this time, especially to the USA and Canada. In just two years he flew more than 500 hours. The aim was to catch up with international developments, and to position the name "Ahlmann" worldwide. On the one hand, together with managers from the Carlshütte, he informed himself in detail about the latest developments in the field of foundry technology and the enamelling industry, as well as in mechanical and plant engineering. On the other hand, new sales markets were to be opened up after those in Eastern Europe were lost behind the Iron Curtain.
In 1951, in the small town of Grand-Mère, in Quebec province in Canada, Severin Ahlmann and an American partner set up Adanac Foundry Industries Ltd, the Canadian subsidiary of the Carlshütte. Hans Schlothfeldt, the foundry manager at the Carlshütte for many years, took over the operational development of the local plant. Grand-Mère marked the beginning of the globalisation of Ahlmann's ventures, which will also play a big role for ACO: a paradigm is established that laid the foundations the later "ACO worldwide".
The 1950s-style illustration of Severin Ahlmann's numerous overseas travels and activities appeared in April 1954 in "Glück auf", the Carlshütte's in-house magazine. This shows an Ahlmann stove in Canada, radiators and shower trays in the USA. While in Mexico and Brazil, Ahlmann bucket loader are at work, and ships of the Ahlmann fleet are sailing in the Atlantic. In 1954, there were already rudiments of what ACO does today in the Americas. The vision of that time has become a reality.
Death of the heir apparent - birth of a new heir in 1952
On the way back from an inspection trip to the Lürssen shipyard in Bremen, Severin's brother Hans-Julius Ahlmann suffered a serious car accident. He lost control of his car and hit a bridge pillar. In hospital he suffered a pulmonary embolism due to shattered tubular bones. He died on 8 January 1952, one month before his 33rd birthday. The family is totally shocked. Many hopes had been pinned on Käte Ahlmann's eldest son. He was already established as a successor in the Carlshütte company.
Three months later, his widow Juliane gave birth to Hans-Julius' son on 14 April 1952. The son is baptized and given his father's name. On 19 April, which has always been celebrated as Foundry Day, the Carlshütte celebrated its 125th anniversary. Severin Ahlmann was now to be appointed as the successor to the family business. Therefore, Käte Ahlmann asked her daughter-in-law, while still in puerperium, to transfer all the new-born’s company shares to Severin. Juliane accepted, and so Josef-Severin Ahlmann entered a new creative phase with extended powers.
The further development of the SAB (ACO) company premises
In 1952, Severin Ahlmann acquired a site from the town of Rendsburg, which enabled SAB to expand decisively.
Just a few months after the start of SAB, it had become clear that the company needed more space for manufacturing. In the second half of 1947, Severin Ahlmann leased space from the neighbouring timber trading company H.F. Timm. This was only a sublease, as Timm itself had leased the land from the owner, the town of Rendsburg.
SAB initially acquired land to the east of H.F. Timm on a so-called expansion site. The tracks of the Carlshütte works railway cut through this area on the northern bank of the Eider. Now the SAB site almost completely surrounded the Timm timber business.
Plan on which - in yellow - the expansion of the young company SAB is clearly visible. Outlined in red is the square that is the subject of the trade between the timber merchant Timm and the town. Yellow is the company Severin Ahlmann and purple is the company H.F. Timm. The buildings in detail: 1) Pipe pressing plant, 2) Severin Ahlmann storage yard, 3) Severin Ahlmann storage yard, 4) Severin Ahlmann storage yard, 5) Carlshütte residential building, now Vorwerk office, 6) Thormann hall (built in 1890), 7) Severin Ahlmann office in the Carlshütte, 8) Horse-keeping yard (ca. 1784), 9) Director's house, 10) Concrete moulding, 11) Sanitary moulding, 12) Sanitary grinding, 13) Haus & Hof Ahlmann, 14) Wagenremise (built in 1913), 15) Alte Meierei.
In the spring of 1951, Severin Ahlmann entered into negotiations with the town of Rendsburg to buy the Timm site – the entire plot, not just the subleased part. In the cover letter, the entrepreneur cites SAB's success story and "great initiative". He also emphasised the future importance of the company for the city and the Rendsburg economic area: greater turnover, more jobs, and higher tax payments could only be generated on the basis of the planned expansion.
In March 1952, the efforts were crowned with success: the town sold Severin Ahlmann a total of four parcels of land totalling 4.3 hectares for DM 350,000. Of this, DM 80,000 for the actual plot of land, and DM 260,000 for various buildings, and DM 10,000 costs for miscellaneous inventory. The existing buildings also included the "Thormannhalle".
Aerial view of the Carlshütte and SAB site, 1950s: 1 Director's house, 2 Old dairy, 3 Stables (built in its first form in approx. 1784), 4 Residence, later new Vorwerk office, 5 Carlshütte main office building, 6 Ahlmann house & farm, 7 Coach house (built 1913), 8 Thormann Hall (built 1890), 9 the Carlshütte.
The first Ahlmann swivel bucket loader 1952/53
Intra-plant transport at both the Carlshütte and SAB was to be rationalised. Severin Ahlmann undertook trips to the USA with Carlshütte executives, such as the authorised signatory Friedrich Sensen, and the foundry manager Hans Schlothfeldt, to look into the rational organisation of work processes there. The team became aware of forklift trucks and bucket loaders, some of which were purchased from the importer Stinnes, and used from March 1952.
The staff were sceptical at first: it was not uncommon to hear "Smiet dat Ding in de Eider!" “Chuck that thing in the Eider!”, when the forklift got stuck on the roads, which, at that time, were not very suitable for vehicles of this kind. But that soon changed to "Where's the forklift?" – so two more pieces of equipment had to be purchased.
The idea arose to manufacture bucket loaders at the Carlshütte. One background to the initiative is that the first dead iron from the cupola furnaces could be put to use as the counterweight. It was Hans-Julius who had the initial idea.
Severin Ahlmann now devoted more time to this topic, especially as his authorised signatory Paul Meyer at SAB relieved him of some of the day-to-day management work. In spring 1952, he entrusted the young commercial employee Rolf Schönrock with a market survey, which turned out to be promising. Severin called together a core team for the bucket loader project. It consisted of the naval architect Hans Boll, who had already proved himself in the construction of the Ahlmann ships COLONIA and CIANDRA, the mechanical engineer Mr. Hoffmann, the driver of the shovel loader at the Carlshütte Mr. Reimers, and finally Rolf Schönrock.
In November 1952, the team travelled to Sweden to inspect the all-round bucket loader made by LECAB. This had a bucket that could be swivelled to both sides. Based on the LECAB shovel, three prototypes of their own Ahlmann swivel bucket loader were to be manufactured by the next industrial fair in Hannover in 1953. An ambitious goal, which was achieved despite some setbacks and internal resistance.
However, the trade fair was not without its mishaps: during the demonstration for a Swiss quarry owner, an hydraulic hose burst. Schönrock quickly distracted the audience, as he himself reported, with "delicacies and alcoholic beverages". Business was done. They generally succeeded in gaining the interest of the public. The first small series production started. The Ahlmann swivel bucket loader began its triumphal procession, and became a synonym for entrepreneurial action, willingness to take risks, the will to diversify, and organisational skills.
AHLMOPLAST - the beginnings of plastics production
Entrepreneurial creativity was also evident when venturing into a completely new material, as was previously the case when the Carlshütte started producing concrete. In 1953, Käte and Severin Ahlmann founded AHLMOPLAST GmbH & Co. KG, which marked the beginning of plastics production in the ACO-Carlshütten cosmos.
It all started with the idea of using glass-fibre reinforced polyester instead of cast iron for the production of bathtubs. However, market demand specifically for bathtubs was still low, so a number of other products were manufactured with the material. These included underwater massage tubs, and modern chairs in the typical style of the time – reminiscent of the designs of Charles and Ray Eames. Light, comfortable and shapely, the seat shells were available in many different colours.
A large order came from the Shell petroleum company: in 1956, the company’s iconic shell emblem made of AHLMOPLAST was presented for the first time. The illuminated logo consisted of two AHLMOPLAST shells illuminated from the inside. Gradually, all large Shell petrol stations were fitted with AHLMOPLAST shells.
AHLMOWELL from Andernach
Plastic production was also started in Andernach. The company produced sheets marketed under the brand name AHLMOWELL, later ACOWELL. As far as is known, this was the first time that the later company abbreviation ACO appears in the form of a brand name.
The AHLMOWELL polyester corrugated sheets produced in Andernach were presented for the first time at the Berlin Industrial Fair in September 1956. They could be produced in many colours, and transparent or opaque, using a manufacturing process developed in-house. They could be used in a variety of ways, e.g., as terrace roofing, windbreaks, or for covered parking areas. For example, they could be found in Rendsburg's open-air swimming pool: a light band made of yellow AHLMOWELL adorned the outdoor pool.
The beginnings of concrete window production
In March 1954, SAB closed a licence agreement for the production of concrete window frames with the Hans Bördlein company, a concrete goods factory located in Reith in Unterfranken, Germany. The windows were intended for building construction, mainly for use in agricultural buildings. At the same time, the company developed its own concrete window construction facilities in Rendsburg for industrial and agricultural buildings, as well as for basements in residential buildings. Over the course of 1956, SAB Büdelsdorf began to produce windows according to its own designs. The licence was soon no longer required.
The decision to enter the window manufacturing business proved to be ground-breaking. The production of concrete windows became the company's "bread and butter business" for more than 30 years. Sales volumes were high, and so were the margins.
It was the far-sighted first SAB managing director Paul Meyer who pushed for this new business field. Years later, Severin Ahlmann wrote to him gratefully: "I often look back on the really great decision years ago to include concrete windows in the manufacturing programme. With the SAB proposal at the time, you made a leap in development possible that was of particular importance to us considering our dependency at the Carlshütte on the somewhat unstable cast-iron washing facilities market."
Concrete window construction opened up a line of continuity that is still alive at ACO today with the plastic window segment.
The SAB (ACO) product portfolio in the 1950s
In the mid-1950s, SAB's portfolio comprised three main product segments: the pure concrete products, the sanitary articles made of artificial stone, and the concrete frame windows.
The start with roof tiles, feeding troughs and simple concrete slabs at the end of 1946 was quickly followed by the production of heavy concrete pipes for water management. Even now, they still make up the majority of SAB's concrete products. Rugged pipes ranging from filigree 100 millimetres to massive 1,000 millimetres in diameter are cast as moulded parts. They are mainly used in sewer construction, or for simple water conduits and house connections, and manholes. There are even manhole rings with diameters of up to two metres for this purpose in the range. Cast-concrete road gullies, kerbstones and pavement slabs are used in road construction. In 1954, the signs pointed to an expansion of production: investments were made in an automatic high-performance press for pavement and floor slabs.
For building construction, SAB produced prefabricated parts made of reinforced concrete and artificial stone. These included staircases - as individual steps or complete systems - frames for doors and windows for installation in the façade, as well as window sills. These articles were mainly used in social housing construction. For example, large apartment buildings in Kiel-Wellingdorf were equipped with ready-to-install structural engineering products.
In addition to the series, SAB also produced tailormade items for the construction industry. For bridge construction, for example, these included cover plates made of reinforced concrete, and sleepers. The construction of district heating pipelines required precast ducts. SAB engineers developed customised solutions for such projects.
An example of artificial stone is marble granules. It differs from heavy concrete in the quality and grain fraction of the gravel mix and the aggregates. Grinding and polishing the moulded parts produces an outstanding appearance and attractive surface properties. Sanitary objects primarily involved large washbasins, circular washing fountains or channels. Also sink outlets, rinsing and washing tubs, and foot and shower tubs. Specialities are worktops for ice cream parlours.
The counterparts to the SAB sanitaryware made of marble granules were provided by the Carlshütte and Ahlmann & Co. Andernach with enamelled cast iron products. The product portfolio of Carlshütte and Ahlmann & Co. Andernach went beyond this. All in all, the three Ahlmann companies offered a diversified range of sanitary and household products. In the 1950s, these could be recognised as branded products because they used the same labels. The products were also presented in a joint catalogue.
Family changes
The Hannover Fair of 1955 was of decisive importance, not only for the success of the swivel bucket loader, but also for the further development of Ahlmann's enterprises. The lady who directed the swivel bucket loader from the upper floor of the trade fair pavilion with her pleasant voice was Maria Jänicke. She was the daughter of a publisher. Josef-Severin Ahlmann fell in love with the attractive and polyglot woman. She became his new partner. In provincial Büdelsdorf, this vision soon caused quite a stir.
Only a few weeks after this encounter - in June 1955 - Severin Ahlmann had a conversation with his mother Käte about the future of the Carlshütte. He probably did not choose his words very carefully, because Käte took it to mean that her son wanted to force her out of the management of the company. She suspected that the initiative for this came not from him but from his new partner. Her relationship with Maria was not on the best footing anyway.
A quarrel ensued, which escalated in February 1956. Käte Ahlmann rescinded the general power of attorney for the Carlshütte granted to her son. Cooperation no longer seemed possible.
In the autumn, Käte proposed a split to her son: Severin should receive the subsidiary in Andernach in exchange for his shares in the Carlshütte. Severin's nephew, the four-year-old Hans-Julius, was now intended as the prospective main heir to the Carlshütte. SAB (ACO) remained unaffected by this arrangement, i.e., continued to be owned by Severin Ahlmann. Severin agreed to the split with a heavy heart.
Between Rendsburg and Andernach 1957 to 1968
Reorganisation of the companies
In spring 1957, the family's companies were reorganised according to Käte Ahlmann's proposal. A contract was signed, dated 4 March.
Severin now had three independent companies: Ahlmann & Co. in Andernach, with its focus on cast iron products, SAB in Büdelsdorf for concrete products, and Ahlmoplast GmbH, with its plastic products.
In December of the same year, Severin and Maria Jänicke married in Munich. The couple moved their centre of life to Andernach. In nearby Bad Breisig, they had a house built by architect Paul Wittig.
Paul Meyer's importance in the management of SAB now increased even more, as its owner was rarely seen in Büdelsdorf. This spatial separation between Severin Ahlmann and the place of his birth remained unchanged until his death.
The Ahlmann sketchbook 1957
The ACO archive includes a unique testimony, the so-called Ahlmann Sketchbook from 1957. It gives an overview of Ahlmann's undertakings at that time in a concise and visually appealing manner. Among other things, it explains how a cast-iron bathtub is made, and how it reaches the customer, the development of the swing bucket loader is shown, as well as the rich portfolio of stoves, concrete windows and plastic products.
Probably this prototype company brochure was never published in this form, as the joint Ahlmann company no longer existed after the split between Severin and his mother Käte Ahlmann.
Developments in Andernach
In 1957, Severin Ahlmann and his former co-partner Hans Günter Möller also went their separate ways at AHLMOPLAST. On 30 May 1957, Severin Ahlmann completely took over the company, which had emerged from the plastics division of the Carlshütte. He moved the company headquarters to Andernach.
In Andernach, the plastics division continued to develop very well. At home, the sheets called AHLMOWELL were supplied to building material wholesalers through a network of agents in Germany. Abroad however - instead of exporting the products - the AHLMOPLAST machines required for production, were sold to licensees, together with the necessary know-how for production.
Already in autumn 1958, Severin Ahlmann could move into his new office in Andernach. The spacious new administration building was an impressive advertisement for the polyester light panels produced at the plant, which were installed in the façade. The new building replaced the temporary offices housed in former military barracks. Three ACO covered car parks made of ACOwell were also built around the building.
Rolf Schönrock left the Carlshütte and, after a brief interlude at another company in Berlin, followed Severin Ahlmann to Andernach. He was entrusted with the expansion of the plastics business in Andernach in 1958.
AHLMOPLAST worldwide: Export of plastics know-how
For the distribution of the AHLMOPLAST systems, Schönrock and a patent attorney developed licence agreements, and he had design documents produced which were to be made available to future licensees for repair and maintenance, and he got to know the market and customers.
The acquisition of licensees was initially concentrated on other European countries. Various building material manufacturers were approached, especially manufacturers of asbestos cement, corrugated sheet metal and corrugated aluminium. The contacts to the ETERNIT Group were important here. After presentation trips in Yugoslavia and Japan, the first contracts were signed at the end of 1959. Especially the trip to Japan was an outstanding experience for Rolf Schönrock. He admired the traditions, and was fascinated by the tremendous modernisation of the country.
The final breakthrough for the distribution of AHLMOPLAST machines came in 1960. Further licence agreements were closed with ETERNIT companies in Norway, Denmark, Sweden, Belgium, France, Great Britain and South Africa. In addition, ASSMANN, a metal and plastics processing company in Graz, acquired a plant.
In autumn 1960, Schönrock flew to Moscow with the technical manager of the Andernach plant, Karl Pulch. Behind the Iron Curtain, too, people began to take an interest in AHLMOPLAST. However, the trip did not lead to a business deal – but at least there was plenty of Crimean sparkling wine and caviar.
In 1961, after a return visit by the Japanese to Andernach, a contract was signed. In the same year, two more production lines were sold to Japan. Licence agreements were also signed with customers in Australia, South Africa and New Zealand - following another trip by Schönrock.
To enable the exchange of experience with the first customers, Severin Ahlmann sent out invitations to the first AHLMOPLAST conference scheduled for 17/18 October 1960. In technical presentations, the attendees gained valuable insights and ideas on the raw materials, the production and the application areas of the products.
The format proved so successful, that another, now much larger conference was held in autumn 1962.
Acquisition of Bördlein, and establishment of the new site in Reith
In the course of 1959, Severin Ahlmann acquired the Hans Bördlein concrete products factory in Reith, Unterfranken. The licences for the concrete-framed windows, which had been produced in Rendsburg for five years, came from this company.
Paul Meyer is the driving force behind the takeover of the former licensor. The window business was going well, and was to be further expanded with the new acquisition. From Reith, SAB could also open up new sales markets in southern Germany.
Concrete windows were now manufactured at two locations, while sales were managed centrally from Büdelsdorf. Reith can be regarded as the first location of the later ACO company outside Rendsburg, as Ahlmann & Co. in Andernach was independent and had other production focuses.
Success in Reith
"Install AHLMANN concrete windows ... and never worry about it again." Not only this advertising slogan, but also the products were convincing. From the beginning, the turnover increased continuously, and soon 150,000 units were sold per year. The return was enormous, and the highest of all the product segments in the company. By way of comparison: the processing of 1 kilogramme of window concrete brought in about 90 pfennigs, whereas the processing of 1 kilogramme of heavy concrete for civil engineering in Rendsburg only brought in about 4 to 6 pfennigs.
The new acquisition was the starting point of the strong expansion in this decade: in terms of sales areas, product range and turnover.
Thus it was window production that created the financial basis for Severin Ahlmann's success in the 1960s.
Change of managing director after Paul Meyer's death in 1962
In Rendsburg, Paul Meyer unexpectedly suffered a heart attack in April 1962 and died, not yet 60 years of age. The experienced managing director was not only the creative heart of SAB from the beginning, he was also a friend of the Ahlmann family. His widow, a sister of Friedrich Sensen, one of the directors of the Carlshütte, was initially able to stay on in the house built especially for the Meyer family on the company premises.
In the dynamic phase experienced by the company at that time, a change of managing director was certainly not beneficial. To avoid a management vacuum after Meyer, Rolf Schönrock took over the management in Rendsburg on an interim basis from January 1963. Together with the Rendsburg management, Schönrock was able to secure the positive turnover and profit situation. In March 1964, he returned to Andernach, as he had long been earmarked to take over the management there.
In January 1964, Heinz Rother succeeded him in Rendsburg. His work for ACO, however, remained a relatively brief intermezzo. He was succeeded by Rudolf Kobelt, the former sales representative for concrete windows.
The so-called Vorwerk office, on the SAB site, which was first occupied in 1962. With its curved outlines, the building reflects the shape of the previous building on the same site. The name Vorwerk refers to the Vorwerk estate on the banks of the Eider – the former farm attached to the old Rendsburg fortress.
Käte Ahlmann's death in 1963 - the end of an era at the Carlshütte
On 5 June 1963, Käte Ahlmann said goodbye to her grandson and prospective successor, the now eleven-year-old Hans-Julius, at Hamburg Central Station. She traveled to Innsbruck to undergo extensive treatment at the clinic of her son-in-law Prof. Max-Joseph Halhuber. Her heart was weakened. Käte Ahlmann's health had deteriorated more and more over the preceding years, not least because the restless entrepreneur did not take it easy. The treatment was ineffective. Only ten days later, on 15 June 1963, she died in Innsbruck.
Käte Ahlmann with the Minister President of Schleswig-Holstein, Kai-Uwe von Hadsel, at the award of the Grand Cross of Merit of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany on 3 October 1960. The picture also shows Dr Marlene Halhuber-Ahlmann; Juliane, now Jebsen; and her son Hans-Julius. Kai-Uwe von Hadsel's connections to the Ahlmann story were manifold. His grandmother was a Thormann, so he came from the family that once owned part of the ACO site. He was also an uncle of Hans-Michael Jebsen, Hans-Julius Ahlmann's half-brother.
Funeral procession for Käte Ahlmann on 21 June 1963 on the Carlshütte site. Eleven-year-old Hans-Julius Ahlmann carries the cushion with the deceased's Federal Cross of Merit. The 3,000 employees of the Carlshütte form a guard of honour. Their long-time confidant Dr Carl Wuppermann speaks at the funeral service. The shadow on the right is cast by the transformer building; the old "sheet metal building" can be seen on the left.
This was not only the end of an era for Carlshütte. The future was also uncertain. In the Christmas edition of the Foundry magazine "Glück auf", published in December 1963 (the first after Käte's death) her daughter Marlene Halhuber-Ahlmann, who now, commuting between Innsbruck and Büdelsdorf, administered the legacy, wrote: "Everyone belonging to the community of foundry people shares our sense of responsibility. Trust me that I take my part as seriously as my mother did, and that I am even more in need of your support!"
The development of cast iron production in Andernach
Cast iron bathtubs remained the most important line of business in Andernach. In 1956, turnover in cast iron bathtubs was DM 10 million, and apart from minor setbacks, it rose steadily over the next few years. In 1968, it amounted to DM 18.2 million. By contrast, turnover in plastic products peaked in 1962 at DM 10.5 million, after which it declined with certain fluctuations.
In 1961, the former foundry manager at the Carlshütte, engineer Karl Pulch, took over the technical management in Andernach. Under his leadership, the automatic enamelling machine was developed in 1962. This technical innovation eased the heavy physical work involved in enamelling the tanks by means of a semi-automatic spreading device with a compressed air sieve. Despite the innovation, and the resulting labour savings, attempts to sell the automatic strewing device abroad failed. In the end, the innovation was only used in the company's own operations.
A few years later, the Carlshütte in turn succeeded in developing an electronically controlled, fully automatic enamelling machine that again reduced the use of personnel for this hard work. Apparently, ACO Andernach and the Carlshütte were engaged in an innovation competition.
The automatic bathtub moulding machine introduced in 1963, on the other hand, proved to be a successful model. In October 1964, ACO Andernach invited the entire German and nearby European wholesale trade to visit the factory.
Over the years, ACO Andernach increased its share of the domestic market, and finally became the market leader for cast iron bathtubs from 1966. Andernach was the first plant to switch completely to titanium enamel, which made a significant contribution to its success. The production facilities for shower trays were also expanded. This investment was completed in 1966, and consolidated the company's pre-eminence in the sanitary sector.
A smaller area of business at the Andernach plant was customised casting, but this remained comparatively small.
At the end of the 1960s, the system of independent sales representatives was disbanded and replaced by ACO sales offices with permanently employed sales staff.
Windows, honeycombs, heavy concrete: Products from Severin Ahlmann Rendsburg in the 1960s
For the Rendsburg site, window production was the most profitable business segment. The product portfolio now included system concrete windows for commercial buildings.
The honeycomb windows made of concrete were a special design. Honeycomb windows were reinforced, window fronts with narrow-profiles used in prefabricated construction. They were statically safe, weather-resistant, and required no maintenance. Here, too, the slogan applies: "Install and never worry about it again!" The range was primarily aimed at the industrial sector, and was used, for example, in factories or in the properties of the German armed forces.
Another special form was widely used: decorative bricks. They were available in trapezoidal, conical or circular shapes, and were used as façade cladding, or to create ornamental light walls, or as decorative elements for staircases, connecting walls and other representative spaces. They could be glazed or unglazed. Architects were enthusiastic about the diverse design possibilities of decorative stones. Decorative stones were often used in religious buildings. In the course of the 1960s, they became a defining element of contemporary architecture.
In the middle of the decade, the product portfolio of the Rendsburg plant also included the traditional programme of heavy concrete production for the northern German region. Marble granule and artificial stone products were also still on the market. However, both took a back seat to the expanding concrete window business.
In 1966, the company employed about 200 people at its locations in Rendsburg and Reith, generating an annual turnover of about DM 10 million. The number of employees shows how high the proportion of manual work still was at this time. In the same year, Severin Ahlmann's plant in Andernach generated a turnover of DM 25.8 million with about 450 employees.
The first step abroad: Sales of concrete windows in Austria 1964
After the production of concrete windows picked up strongly at the beginning of the 1960s, especially at the still young Reith site, Severin Ahlmann took a forward-looking step: for the first time, a concrete product was to be sold abroad. At the Munich exhibition of the German Agricultural Society in 1963, a special interest in Ahlmann's barn windows was observed among Austrian farmers. The decision was therefore made to supply the Austrian market with concrete windows as well.
A suitable distribution partner was found in Gebr. Assmann & Co. in Leibnitz, Styria. The cooperation was initiated at the beginning of 1964, when the current interim managing director, Rolf Schönrock, contacted the industrialist Dr. Emmerich Assmann. Assmann's Graz plant was already the licensee of an AHLMOPLAST plant. Now the business relationship was to be extended to the window sector. After the customs situation had been clarified, sales in Austria began in the middle of 1964. However, there were no explicit plans for a licence or own production in the neighbouring country. It was rather a question of utilising the capacity of the factory in Reith or expanding there.
1965 First use of the ACO logo lettering for Rendsburg
The different names of the individual companies – Severin Ahlmann Rendsburg, Severin Ahlmann Reith, and Ahlmann & Co. Andernach – were confusing and unintuitive for the market. For this reason, the abbreviation ACO for Ahlmann & Co. Andernach was gradually introduced as the brand and logo for all three companies. ACO was to become an unmistakable brand with a strong recognition value.
The further development of plastics production at ACO Andernach
The 1960s were marked by a series of pioneering innovations in the plastics sector at ACO Andernach. In 1965, ACO was the first company on the German market to develop shower partitions, called ACO TRENN. The partitions made of shatterproof fibreglass were in line with the trend for more comfort in the bathroom. A significant increase in sales was achieved here, and by 1974, the company had a market share of 20 percent.
The importance of plastics production was not limited to the Andernach plant. In 1968, process engineer Heinz Dieter Brink from ACO Rendsburg went to Andernach to familiarise himself with plastics. Here he got to know the corrugated polyester sheet production. The connections and communications between Rendsburg and Andernach were lively. Back in Rendsburg, he combined the core competence of concrete in Rendsburg with the plastics competence from Andernach. On this basis, something completely new and innovative was to be created in 1969: the first ACO channel made of polyester concrete.
Experiments in the plastics sector
In 1958, the then managing director of Ahlmann & Co. Andernach, Mr. Simmat, proposed to produce plastic tiles according to the American model, and to establish them on the German market. The idea was based on the assumption that cumbersome tile removal during bathroom renovations could be avoided by using easy-to-glue plastic tiles. Production was started, and even a mail-order company for plastic articles was founded. Plastic tiles, however, do not go down well in Germany. Consumers stuck to ceramic tiles, and so production was eventually stopped.
The attempt to manufacture sports boats from glass fibre-reinforced plastic, which began in 1966, was also unsuccessful. At the international boat show in Hamburg in 1967, a large houseboat, a sailing catamaran, an open motorboat, a fishing boat, a bathing island, and a jetty were presented.
The idea sounded promising at first: the boats were supposed to be light and cheap to produce. However, the material turned out to be unsuitable. Mr Weber, Severin Ahlmann's driver, got into distress on a test trip, and involuntarily met seals on a sandbank off Sylt before he was rescued. The plastic boats did not have sufficient stability, and production was discontinued. Nevertheless, Severin Ahlmann was still convinced of this project later on. In his autobiography from 1999, he wrote that it was a big and expensive mistake to abandon the leisure catamarans.
Start of garage production in Rendsburg in 1968
The end of the 1960s saw a turning point at ACO: heavy concrete production for water management in the Schleswig-Holstein sales region was discontinued in 1968 for reasons of market policy and investment strategy. This marked the end of an important tradition in Rendsburg: the company's history began 20 years earlier with such slabs and pipes.
At the same time, in spring 1968, Severin Ahlmann introduced a new product to the line of concrete articles: garages. Like the original window production in the mid-1950s, this product was not an in-house development by Ahlmann, but was licensed. The licensor of the garage production was J. Kaletka, Ing.-Büro für Bau- und Betriebsplanung, IBK for short, in Gaggenau, Baden.
The concrete system garages were completely prefabricated in the factory, then transported to the customer by truck, and erected on site. These were really large items that ACO now delivered to the licence area, almost all of Schleswig-Holstein, initially with the exception of some regions north of Hamburg.
Garage production flourished, and the product was given the name "ACO Stabil". The ACO garage quickly established itself as a pragmatic and cost-effective solution for parking cars. It was produced in Rendsburg for almost a decade.
Launch and first successes of ACO Drain 1969 to 1974
ACO Drain: Idea and product
At the end of the 1960s, surface drainage was still mostly point-based. This involved draining from individual gullies by way of buried drainage pipes. According to this approach, the water had to reach the lowest points on the surface, which was why cross gradients were required over large areas. The new concept of linear drainage using long drainage channels was the much more elegant solution.
It was two independent sales representatives, Eberhard Grundmann and Fritz Fiedler, who approached the head of ACO Sales, Karl Arno Ebsen, with the idea of drainage channels. A new, innovative product idea was being sought, because at this time, window production had passed its zenith. A kick-start was given by the garage sector. Here the question arose of how best to realise the drainage in front of the prefabricated garages.
Drainage channels were already available on the market. ANRIN, for example, produced a 1 m long asbestos cement channel made of pipe half-shells, with glued-on side walls made of asbestos sheets. Arno Ebsen approached ACO engineer Dieter Brink in Rendsburg. Brink developed the original idea further, for example, by turning the pipe half-shells into pipe third-shells, with glued-on side walls with a length of 1.2 m.
Severin Ahlmann had yet to be convinced. The failure of the catamarans still sat deep. After hesitating for a while, he gave the green light for the start of channel production. The innovation was introduced on 1 May 1969, already under the product name ACO DRAIN, which is still in use today.
It quickly became clear that ACO channels were easier to handle than conventional channels: they did not require any formwork on site. In addition, the channel was lightweight. "The advantage of our channel lies in the special construction ... as well as in the low transport weight. Compared to conventional channels that are shuttered on site, our channel is cheaper because ... the channel does without," said Arno Ebsen.
ACO DRAIN was a decisive turning point in the history of ACO. The product would shape the future direction of the company. In the following years, ACO developed from a building materials generalist with a focus on window production, into a specialist provider of drainage solutions.
Abb. The first brochures for ACO Drain in 1969. At the beginning, the main material was fibre cement, also known as asbestos cement or Eternit. The raw materials were pipes and sheets made of this material. They were supplied directly by a manufacturer in Bremen. In the cutting department at ACO, the asbestos pipes of 1.20 metres length were then cut with a milling machine. This produced one-third shells, which were glued to the cut panels on the long side, and fitted with the metal gratings on the open side in the same way.
Customers and first sales success
In principle, the drainage channels were aimed at the specialised building materials trade, as well as construction companies. Building authorities and industrial architects were also interested.
It was understandable that special advertising efforts were being made with all planning authorities in mind, and that users and architects were also being addressed directly. Federal and state building authorities, as well as road construction authorities were sent brochures, as were mineral oil companies that build petrol stations. In addition, the car industry was addressed because it was involved in the planning of garages.
In the year of the market launch, i.e., from May to December 1969, ACO achieved a turnover of DM 260,000 with the DRAIN channel. A phenomenal success!
Adjustments needed - new material, polymer concrete
The response to the DRAIN channels at the Constructa building trade fair in Hannover at the end of January 1970, not to mention the sales to date, the results of market research, and the advertising channels that were used at the time, were certainly promising. But the first problems arose a few months after the start of production. The channel proved to be unstable. The Achilles' heel of the construction was the bonding. Adhesive surfaces that were too small, caused the frequent collapse of the gratings under load. In addition, fibre cement panels were inflexible when it came to forming. Thus, less than a year after the market launch of the channels, a change in the production process was on the horizon. Both the material and the forming were being optimised. Dieter Brink's team had a favourite as the new material: polymer concrete. This would make it possible to cast the channels in their entirety instead of gluing them together.
ACO already had experience in the production of GRP moulds with a backfill of sand mixed with polyester resin, i.e., polyester concrete, because of the concrete honeycomb production using the vibro-pressing process. This was the area of expertise of the ACO model maker Gerd Grabow. Dieter Brink came up with the idea of using the new material for the channels. This was therefore where the expertise from plastics production in Andernach was combined with the concrete know-how in Rendsburg.
ACO needed a special mixing and casting machine for the series production of polymer concrete channels. Only a system from RESPECTA came into question. The machine manufacturer from Wülfrath was only founded in 1969, and specialised in plants for the preparation of highly reactive mixtures. The tip about the new technology came from the Austrian sales partner Assmann.
The new machine was installed in Rendsburg on 9 March 1970. It still had a few teething problems – such as the central screw conveyor clogging up too quickly – but ACO's plant engineers found a solution.
The Respecta machine was stationary. Only its movable pouring nozzle could be moved to the moulds. The initially wooden DRAIN moulds were turned upside down and filled with the viscous mass from the open underside – which was somewhat awkward. ACO's plant engineers soon constructed a new, dedicated and fully mobile machine, that moved along the production line and filled the moulds. After only 10 to 15 minutes, the strength of the channels was enough to allow the moulds to be opened.
The length of the first channels corresponded to the previous asbestos cement channels. They had a wall thickness of 15 mm. In autumn 1970, the production of ACO Drain NW100 could be completely converted to polymer concrete. The material used in the early days - fibre or asbestos cement – became obsolete.
The improved properties of the new material - greater stability and resistance - convinced the customers. In addition, a far greater variety of articles was possible with the polymer concrete casting material. If the construction of moulds and the casting succeeded, all variations were conceivable. This laid the foundation for a wide range of drainage solutions.
ACO and the Olympic Games - the beginning of a success story
In the spring of 1970, ACO received a spectacular major order: the Rendsburg company was to equip the new Olympic Stadium in Munich with ACO DRAIN for the 1972 Olympic Games. But it was not just about equipping the stadium, but also ancillary facilities in Munich, and stadiums at other venues. The initial volume of 1,300 metres of drainage channels was to be followed-up by an order for a further 1,000 metres. For ACO Drain's marketing and prestige, the order was phenomenal. Anecdotes and legends surround the contract negotiations with the Olympic construction committee, and the first delivery to Munich. For ACO, there was also a lot of luck involved. In the end, the superiority of the polymer concrete material was convincing. "That was sensational. Something like that doesn't happen very often in German industrial history," recalls long-serving Sales Manager Arno Ebsen.
Munich was followed by other Olympic Games for ACO: Montreal 1976 would be the first appearance in North America. Over the years, ACO would equip all the Olympic Games - except the Olympic Games in Moscow. Stadiums for football world championships all over the world follow. The equipping of large arenas with drainage technology also involves completely different components that can also be made from polymer concrete: the perimeters of running tracks, and jumping-off beams for instance. This was how the company established its ACO SPORT range in the mid-1970s.
Ernst Vollstedt - the father of the global success of ACO Drain
At the end of the 1960s, when the retirement of Rendsburg managing director Rudolf Kobelt became imminent, Severin Ahlmann had to establish a successor, and his choice fell on Ernst Vollstedt, who was barely 30 years old. At the beginning of the 1970s, Vollstedt, a native of Rendsburg, took over the management of the site on the Kiel Canal.
Vollstedt was born in Rendsburg in 1938. After completing his schooling and military service, he started working for the Severin Ahlmann company on 1 April 1960, not in Rendsburg, however, but at the new site in Reith. Barely two years after completing his training, he took over the management of the company at a young age. He interrupted his time in Reith in 1965, for a four-month assignment in the USA.
In 1967, Vollstedt moved to Andernach to set up a modern logistics operation. After completing this work, he finally returned to his home town with his family in 1968, and started at ACO Rendsburg.
In June 1969, at the age of 31, Ernst Vollstedt took over responsibility for the Rendsburg site. At the beginning of the new decade, Severin Ahlmann's centre of life was still in Andernach, in the Rhineland, but he spent more and more time in Pöcking on Lake Starnberg, and in Morsum on Sylt. After a series of personal crises - the failure of his second marriage, and the decline of the Carlshütte - Severin Ahlmann travelled a lot, with long stays on the Fiji Islands, and in the USA, for example. The two managing directors - Rolf Schönrock in Andernach, and Ernst Vollstedt in Rendsburg - ran the companies.
Vollstedt kept his boss informed of developments in detailed letters. Later he started to write two to three reports a year on all the company's business segments.
In the first few years under the aegis of Ernst Vollstedt, ACO rapidly developed into one of the leading suppliers in the drainage solutions market. With product manager Dieter Brink, sales manager Arno Ebsen, and system designer Uwe Wunderlich, Ernst Vollstedt made ACO-Drain a global success.
ACO Drain goes international
For ACO DRAIN, the Rendsburg company entered into a sales partnership in Switzerland at the end of 1970. Studer und Thomann AG took over sole distribution for Switzerland, and from April 1973, also for neighbouring Austria.
A second sales cooperation was established in France. The contract with the Ets. R. Lefèbure group, based in Mantes-la-Jolie in the Île-de-France region near the capital, came into force on 1 April 1972. Behind the group was the Lefèbure family of entrepreneurs. Vollstedt later convinced his boss Severin Ahlmann to set up a plant in France with Lefèbure.
The first launch of ACO DRAIN in a northern European market took place in neighbouring Denmark. The Danish region had long been familiar to the Ahlmann family of entrepreneurs. From 5 June 1972, Sapolite A/S became the sole distributor for ACO DRAIN. Over the next few years, other polymer concrete products were added, such as the ACO Farm range.
The first steps with DRAIN were taken in England at the same time. At the beginning of 1972, a partnership was formed with the businessman Malcolm Henderson, who organised the market launch, particularly in the London area. Consideration was given to setting up their own production in England, but the plan was shelved. The search for a distribution company was unsuccessful. Malcolm Henderson therefore founded "Kaskade Drains Limited" in mid-1973, which sold ACO DRAIN channels mainly in southern England. The sales figures were promising. Kaskade was able to place ACO drainage systems well in England by the summer of 1974. Around 50 major construction projects were supplied by then, including some involving prominent clients such as British Railways, or the London Port Authority.
Drainage instead of silk printing - production in Mitlödi, Switzerland
Now that a number of European markets had been opened up through sales cooperation agreements, production of ACO DRAIN was also to be established abroad. An opportunity presented itself in Switzerland in the spring of 1972. The silk printing company Mitlödi AG, located in the small town of Mitlödi in the canton of Glarus, was looking to expand its production range.
The traditional Swiss silk and textile industry was in crisis. The whole sector had to reorient itself, and also open up business segments outside the traditional business.
The contact came about because Severin Ahlmann sent numerous airmail letters to potential interested parties. As always, they were written in green ink, indirectly marking his leadership position. Green was traditionally reserved for the top management level in Germany's administrations. Dr. Kurt Hauser of Seidendruckerei Mitlödi AG was interested and replied.
The deal was sealed in June 1972. The silk printing works, in which Severin Ahlmann had a one-third share, invested heavily and made a new factory building available in Mitlödi. ACO technicians assembled the machinery by the beginning of February 1973, and then also mentored the first two weeks of operation on site. At the same time, three Swiss employees were trained at ACO in Reith. The metal cast gratings were supplied by ACO Andernach. One month earlier than originally planned, production of ACO DRAIN started on the new production line on 5 February 1973.
For the time being, the sole distributor in Switzerland was Studer und Thomann AG, which no longer bought its channels from ACO in Germany but from the canton of Glarus. As early as spring, Mitlödi had to increase the production output of channels from the originally planned 420 m per day. In 1974, the first full year of production, the "silk printing works" made a net profit of 226,000 Swiss francs on sales of over 2.5 million Swiss francs.
Attempted reunification: Andernach and the Carlshütte
At the turn of 1970/71, Severin Ahlmann approached his sister Marlene Halhuber-Ahlmann to propose that the Andernach plant be reunited with Ahlmann Carlshütte in Rendsburg. Marlene Halhuber-Ahlmann’s first husband, Rudolf-August Oetker – the owner and head of the Bielefeld-based Oetker family business, and an expert in mergers and acquisitions – was called in together with his M&A team as a mediator. However, Severin Ahlmann's economic advisor Arno Seeger advised against it in view of the economic situation at the Carlshütte: merging a healthy company with a "sick company", could cause both to go under.
In the end, the reunification plans do not fail because of this reservation, but because a rejection came from the Carlshütte: the investments recently made in Andernach and the resulting credit burden, were not looked on favourably by the people in Rendsburg. Moreover, it was becoming apparent that an agreement on the purchase price was hardly possible: the perceptions on both sides were too far apart.
Expansion of the product portfolio in Andernach
In Andernach, the ACO-TRENN shower enclosure designs with aluminium profiles and new panel material were launched. At the 6th International Sanitary and Heating Fair in Frankfurt in 1971, the corner cubicle in particular attracted a lot of attention. Another novelty in the TRENN programme were special bathroom modules for hotels and for the renovation of old buildings. In the same year, the new prefabricated balcony and terrace partition ACO-PRISMA was launched.
The increase in turnover in Andernach was enormous: from DM 32 million in 1970, to an incredible 51.1 million in 1973, i.e., a rise of 60 percent within only three years.
Bathtubs continued to make up the bulk of the turnover, with sales increasing by almost 70 percent in the three years mentioned. Business with boilers developed even better, even though their share of total sales was considerably lower at 7.6 million. Their sales quadrupled compared to 1970. The sales of ACOWELL however were declining.
The positive development was due in no small part to the Social Democrats, previously so criticised by Severin Ahlmann: in the first years of the Brandt government, the number of completed flats in the Federal Republic rose from less than 500,000 in 1970, to more than 700,000 in 1973 - never before or since has a higher figure been reached. The housing boom had a direct impact on the order books at ACO Andernach. Bathtubs, boilers and shower enclosures were in big demand.
Arno Seeger - Severin Ahlmann's general agent
In January 1973, due to health problems, Severin Ahlmann appointed his close confidant Arno Seeger as general agent and sole member of the Board of Directors for the plants in Andernach and Rendsburg. He himself retired to sanatoriums, first to Bad Reichenhall, then to Königstein im Taunus.
Arno Seeger, born in 1914, studied economics and business consultancy, and was quite well known in business circles. He was considered a "string puller", and belonged to the exclusive circle of grey eminences of the German economy. Seeger sat on many supervisory boards, advised companies along the Rhine, and was also very well connected in political circles. He began his career at Deutsche Bank. He later served as head of finance at Krupp, but left the company in the wake of the Krupp crisis in 1967. A short time later, he joined the Quandt Group as an intermediary. Seeger was also referred to as a "businessman without a business".
Two anniversary celebrations: 25 years of ACO
In October 1973, ACO Rendsburg celebrated its 25th anniversary with a big party at the Baltic Sea resort "Damp 2000". But why in 1973? – after all, SAB was founded in December 1946, so the celebration should have been at the end of 1971. In fact, it was ACO Andernach whose anniversary was celebrated in 1973! 1 November 1973 was the 25th anniversary of the establishment of ACO in Andernach. Severin Ahlmann had decided to celebrate both anniversaries in the same year, and not separately, even though this meant a two-year delay for ACO Rendsburg.
First, the company founder invited the employees of Rendsburg and Reith, together with their spouses, to a long weekend at the Baltic resort "Damp 2000" from 25 to 28 October 1973. The gigantic holiday resort on the Schwansen peninsula on the Baltic Sea had only just been opened. For the employees from Reith, there was a tour of the factory in Rendsburg beforehand. They celebrated for three days in the hotel complex. Room and board were free for the employees. All the hotel's leisure facilities could be used. The celebrations were legendary, and people at ACO still talk about Damp today. Severin Ahlmann shone with his engaging, charismatic personality.
A week later, there was also a day and a half of celebrations in Andernach. A small tent city with a restaurant, dance hall and a circus were set up in the company grounds. The renowned caterer Käfer from Munich-Bogenhausen, took care of the catering. Severin Ahlmann gave one of his famous humorous speeches. From the family circle, his now 21-year-old nephew Hans-Julius Ahlmann, and Severin's niece Katharina Halhuber-Ahlmann, the eldest daughter of his sister Marlene, also took part.
When part of the tent city burnt down in the night after the end of the celebrations - the cause of the fire could not be clarified - it seemed like a bad omen for what would happen in Rendsburg a few days later.
The explosion incident in Rendsburg
On 9 November 1973 at 12:38 p.m., a "violent bang" startled Büdelsdorf. Immediately, "a huge jet of flame" could be seen over the ACO site.
An explosion in the ACO DRAIN production factory! Chemicals for the production of the polymer concrete mixture exploded. Part of the building was immediately destroyed, and the resulting fire led to further destruction. 14 employees were in the building at the time of the explosion. The accident occurred shortly after the shift change at the stationary plant. ACO employee Uwe Wunderlich immediately alerted the Büdelsdorf fire station, which really quickly started extinguishing the fire.
Severin Ahlmann's sister, the doctor Dr. Marlene Halhuber-Ahlmann, was not far from the scene of the accident in her parents' house on the neighbouring Carlshütte site, and rushed to the scene of the accident where she administered first aid. Severin Ahlmann was in Andernach at the time of the explosion.
Nine people suffered severe burns, and another three minor burns and injuries. Reinhard Kirschkowski died directly at the scene of the accident. In addition to the fire brigade and rescue workers, the criminal investigation department was soon on the scene, questioning the employees who had been present.
A few hours after the explosion, workers Albert Bahrt, Herbert Jasker and Günter Noch, died from their injuries, in the Rendsburg city hospital. One week later, Dieter Schmidt also died in the Berufsgenossenschaftliche Unfallklinik in Ludwigshafen-Oggersheim. A total of five people lost their lives.
Aftermath of the accident
The accident had a direct impact on the company's approach to hazards and safety. Until that autumn in 1973, there had been no major accidents at ACO - despite the predominantly strenuous physical work, as well as the multiple use of heavy equipment. The relatively new source of danger, chemicals for resin production in polymer manufacturing, had been well under control up to then - for more than three and a half years.
The first consequence of the explosion in Rendsburg was the shutdown of polymer concrete production in Rendsburg, then also in Reith. The safety measures were reviewed and modified. Standards were raised to the highest level in cooperation with the Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing.
On 21 January 1974, DRAIN production in Reith was restarted. And in Rendsburg a new concept of polymer concrete production with increased capacity was implemented at the beginning of April 1974.
Acrylic bathtubs - the missed opportunity for ACO Andernach
After rival companies such as Hoesch and Kaldewei launched acrylic bathtubs - as an alternative to the traditional cast iron bathtub - ACO presented the first round bathtub made of fibreglass polyester, with only an acrylic gelcoat, at the 1973 Frankfurt sanitary trade fair. Managing director Rolf Schönrock, however, did not consider such a niche product to be sufficient. He wanted to get into acrylic bathtub production.
On Schönrock's initiative, negotiations about a cooperation were held with the Scottish bathtub manufacturer Carron. Carron was initially to produce acrylic bathtubs for ACO for sale on the German market in two standard sizes. Then the Scots were to help set up ACO’s own acrylic bathtub production in Andernach. But this would require considerable investment. Severin Ahlmann hesitated. When the negotiations with Carron reached the crucial phase at the beginning of 1974, the company owner was on business overseas General manager Arno Seeger hesitated to make such a far-reaching strategic decision without consulting the company owner. No deal was reached.
In his autobiography, Severin Ahlmann retrospectively described it as a "serious entrepreneurial mistake" not to have started production of acrylic bathtubs.
The Carlshütte in the 1970s
DThe Carlshütte underwent a cautious modernisation process in the late 1960s and early 1970s after a long standstill. Its main product was still bathtubs, but other traditional branches of production, overtaken by market developments, were gradually abandoned. This included, for example, the production of stoves, which ended in 1972.
At the same time, new segments were opened up. Continuous casting, i.e., the production of prefabricated raw material and semi-finished products from iron alloys, proved to have a promising future. However, it required significant investments in new plants.
In 1970, the foundry built a continuously operating cupola furnace with a capacity of 9 to 15 tonnes per hour for DM 8 million. Four electric induction furnaces were installed downstream. The new facilities, with contemporary dust removal technology, were also good for the environment - the air quality in Büdelsdorf and the surrounding area improved considerably.
Although the name Carlshütte was still very much present, the company now traded simply as Ahlmann GmbH. The production of swing loaders, which started in the early 1950s, had been outsourced to the independent company Ahlmann Maschinenbau GmbH since 1972. Here the company was doing successful business with the completely newly developed AS 7 and AS 12 models, which went into series production in 1969 and 1972 respectively.
Ahlmann GmbH wanted to open up a new promising business segment with the production of prefabricated baths. After one year of development, the Ahlmann complete bath was presented at the 1973 International Sanitary and Heating Fair in Frankfurt, under the name "Badinet". A little later, shipyards also approached Ahlmann with the request for prefabricated bathroom solutions. The Badinet was further developed into the Marinet, a prefabricated bathroom module for shipbuilding.
Ahlmann's stand at the 1973 International Sanitary and Heating Fair in Frankfurt. Glück auf!" noted: "The Ahlmann stand was again a special attraction. At the old location, but with a new face and real surprises. The "Badinet" alone, fully equipped and "with live models", caused a stir, not only among the sanitary specialists: a catwalk that allowed educational insights from a bird's eye view had to be temporarily closed..
Crisis at the Carlshütte
In the midst of the restructuring process that the Carlshütte was undergoing, the Federal Republic was rocked by the biggest economic crisis in its experience. In the spring of 1973, the Bretton Woods world monetary system collapsed. Until then, this had stimulated world trade by largely stabilising exchange rates, and made it largely independent of exchange rate risks. Now the value of the German mark rose considerably against the currencies of the most important trading partners, for example, by more than double against the US dollar.
For an export-oriented company like the Carlshütte, which marketed its products worldwide, this was a disaster. Carola bathtubs, for example, became more expensive abroad. At a stroke, they were no longer competitive on the world market.
Then there were the new products from competitors. These were the classy plastic bathtubs mentioned above, and the enamelled steel bathtubs produced in large quantities, especially by Kaldewei. These were lighter than cast iron bathtubs , and were therefore easier for plumbers to handle.
The first oil crisis also followed in 1973. It was triggered by the Organisation of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), whose members decided in October to cut their production in response to the Yom Kippur War, in order to exert political pressure on the West. Within a few months, the price of crude oil quadrupled, and the prices of other commodities also continued to rise. Economic activity dived to an extent unprecedented in the history of the Federal Republic in 1974, especially in the construction industry, which was so central to Ahlmann.
Bankruptcy of the Carlshütte in 1974!
In September 1974, the companies Ahlmann GmbH and Ahlmann Maschinenbau GmbH, which had emerged from the long-established Carlshütte, had to file for bankruptcy after almost 150 years of successful operation. The Ahlmann family left the Carlshütte. The Hamburg ship salvage entrepreneur Ulrich Harms bought the Carlshütte at a "junk price", as the news magazine DER SPIEGEL put it. He paid DM 13.7 million.
After considerable investment and restructuring, the Carlshütte could continue to operate with a significantly reduced number of employees, and a changed product range. The focus was still on foundry, mechanical engineering and sanitary ware.
In 1998, Harms also went bankrupt and died. The Carlshütte was dissolved and sold at auction. It was Hans-Julius Ahlmann who bought back the site and buildings, so that ACO and the Carlshütte were finally reunited geographically and idealistically. Since then, the historic aisles and the grounds of the Carlshütte have been filled with new life, now as a venue for NordArt, one of the largest exhibitions of contemporary art in Europe also known as Kunstwerk Carlshütte.
The sale of ACO Andernach
The bankruptcy of his parents' company, the Carlshütte, plunged Severin Ahlmann into a serious personal crisis. He felt guilty. In addition, he divorced his second wife Maria in the same year.
The economic crisis also affected ACO Andernach. In the course of 1974, there was a massive slump in sales. The optimistic growth targets were suddenly a long way off. Only three weeks after the bankruptcy of the Carlshütte - at the beginning of September - Arno Seeger offered to take over the Andernach plant at a very favourable price, namely only DM 1 million. On 23 September 1974, the contract was signed. Seeger had the right to use the old company name and the ACO brand name until 1982.
Thus, in 1974, the entrepreneurial activity of the Ahlmann family also ended in this company.
Review and outlook: ACO on the road to success
From 1974 onwards, Severin Ahlmann's entrepreneurial activities were concentrated entirely on ACO in Rendsburg, which was founded in 1946, and its branch factory in Reith in Lower Franconia. A magical rise began for the small company ACO. In eight years, sales rose from DM 12 million to DM 43 million, largely driven by ACO Drain.
This success bears a number of names: at the top, the young, highly dynamic managing director Ernst Vollstedt, a true ACO homegrown, the great sales director Karl-Arno Ebsen, the father of the ACO Drain channel system Dieter Brink, and Uwe Wunderlich, the builder of the first polyester concrete plant. All four of them are still around, and in their retirement, can look back with immense pride on achieving this unique success in their lifetimes.
At the end of 1978, however, the run was over for a while. It did not go much higher for the time being. With the establishment of ACO companies in Switzerland, France and the USA, and numerous foreign agencies, the company had perhaps overstretched itself somewhat, and needed a breather.
When Hans-Julius Ahlmann politely asked his uncle in the course of 1980 whether he could use him - he was employed by MAN in Augsburg at the time - he immediately agreed. On 2 May 1981, Hans-Julius Ahlmann started work in Rendsburg.
In the 40 years since then, ACO has grown into a large company, positioned worldwide, with a very strong brand and a turnover of 1 billion. This has been made possible by our employees, a lot of luck, and our corporate culture, which tries to bring out the entrepreneurial spirit in as many of us as possible. And some of us have been able to realise their own entrepreneurial visions of a lifetime. So may it continue... And the first billion, they say, is supposed to be the hardest…
Today, the ACO Group is represented with sites and production facilities in more than 40 countries. See also ACO group worldwide.
The ACO Wiki does not end here, it remains exciting right up to the present day. It will be expanded step by step in the coming months with more history and stories from and about ACO.
Enjoy reading, browsing and discovering!
Your ACO Wiki Team
Imprint and Picture Credits
Here you find the imprint and picture credits.